#Urine #urine_examination #urine_test #microbiology
Urine Examination?
Urine analysis?
Physical examination of urine ?
Urine test in hindi
What is urine
What are 4 types of tests done on urine?
Microscope examination of urine
Chemical examination of urine
Glucose test of urine
Protein test in urine
Bile pigment
Bile salts
Colour of urine
Volume of urine
What is complete urine examination?
What are normal urine test results?
How to read urine report ?
What can you examine in an urine?
What are 4 types of tests done on urine?
What can be detected in a urine test?
What is normal urine test report?
How many types of urine tests are there?
Red blood cell urine test.
Glucose urine test.
Protein urine test.
Urine pH level test.
Ketones urine test.
Bilirubin urine test.
Urine specific gravity test.
What can be detected in a urine test?
Can I drink water before urine test?
Can urine test show kidney problems?
How to find UTI infection
What is UTI
What are the first signs of kidney problems?
What does high protein in urine test mean?
What is a normal urine protein level?
What causes glycosuria?
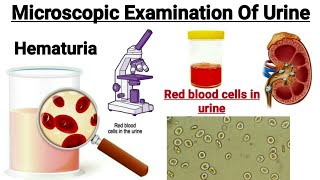
Hematuria
Kitonuria
Urine For Specific Gravity And Its Significance
Urine Bile Salts And Bile Acid Metabolism
Urine For Bile Pigments (Bilirubin, Urobilinogen, And Bile Salts)
Urine 17-Ketosteroids Level (24 Hours Urine)
Urine Amylase (Amylasuria), Amylase/Creatinine Clearance Ratio
Urine Sodium (Na+), Spot Test, Or 24 Hours Urine Sodium
Urine Protein 24 Hours Sample, Classification Of Proteinuria
Urine Potassium (K), Quantitative 24 Urine Or Random Sample
Urine Protein (Proteinuria), Spot Test For Urine Protein, Microalbuminuria
Urine 24 Hours Collection With Instructions
Urine Albumin (24 Hours) Or (24 Hours Protein)
Urine Calcium (Ca), (Quantitative 24 Hrs Urine Calcium)
Urine Bilirubin, Bilirubinuria
Urine For Screening For Drugs, Drugs Abuse, Opiates, Cocaine, Marijuana, Amphetamines And Other Stimulants
Urine For Ketones, And Ketone Bodies (Ketonuria)
Urine PH And Its Significance
Urine, Uric Acid Quantitative (24 Hrs Urine Sample), Uricosuria
Urine For Phosphorus (Phosphates), 24 Hours Urine Sample
Urine For Urobilinogen And Ehrlich Reagent
Urine 24 Hours For VMA (Vanillylmandelic Acid), Catecholamines (24 Hours Urine), Neuroblastoma
Urine Analysis:- Complete Discussion (Part 1)
Urine For Pus Cells, WBC, Eosinophils, Mononuclear Cells, Pyuria
Urine Formation, Types Of Urine, And Urine Preservatives
Urine Analysis:- Physical Examination, And Interpretation (Part 3)
Urine History, Urine Composition, Normal Finding, Advantages Of Urine Analysis
Urine Changes When Urine Left At Room Temperature, And Preservatives
Urine 24 Hours Urea, Urine Urea Nitrogen/24 Hours
Urine Analysis:- Microscopic Examination, And Interpretations (Part 2)
Urine Crystals (Crystalluria)
Urine Analysis:- Chemical Examination And Interpretations (Part 4)
Urine Normal Values, And Their Significance
Urine Sample Types, Urine Formation, And Composition
Urine For Bile Pigments
Sample For Urine For Bile Pigments
The sample is urine.
Bile salt can be checked on random urine.
Bile pigmetns also include bilirubin and biliverdin.
Indications Of Urine For Bile Pigments
This is because the presence of bile pigments in the urine indicates liver dysfunction.
The presence of bile pigments in the urine helps to diagnose the increased production of bilirubin.
Pathophysiology Of The Bile And Bile Pigments
Bile acid and bile salts are used as synonyms.
The bile is a fluid synthesized by the liver and consists of :
Conjugated bile salts.
Bilirubin diglucuronide.
Cholesterol.
Phospholipids.
Electrolytes.
Water.
Bile is alkaline due to the presence of bicarbonate.
Bile color is golden-brown to greenish-yellow and has a bitter taste.
Urine Analysis
Urine Microscopic Examination
Sample For Urine Analysis
Freshly voided urine is the best sample.
If delayed, then refrigerate the urine.
The best volume for the centrifuge is 10 to 12 mL.
Factors that will interfere with the urine analysis:
Dysmorphic RBCs:
These RBCs vary in size, have cellular protrusions, or may be fragmented.
Wright’s stain can also help to differentiate these RBCs as hypochromic and prominent cellular blebs and protrusion.
Macroscopic hematuria:
It shows cloudy urine with a red to brown color.
This is seen in:
Trauma.
Acute infection.
Inflammation.
Coagulation disorders.
Microscopic hematuria is seen in:
Glomerular diseases.
Malignancy of the urinary tract.
Renal calculi.
The possibility of menstrual contamination should be considered in females.
Hematuria may be caused by:
Renal disease
Infections
Renal stones
Renal tumors
Bleeding disorder.
Anticoagulant therapy.









Информация по комментариям в разработке