Welcome to my channel ''Lectures of Physics". This channel contains lectures of physics on class 9th, 10th, 11th and 12th in easy way.
This video is about power class 9 physics chapter 6 work and energy.
"Power" has multiple meanings, including the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred (measured in watts), the ability to influence people or events, and the product of multiplying a quantity by itself (e.g., x² is x to the power of 2). The specific definition depends on the context, such as in physics, social dynamics, or mathematics.
In Physics:
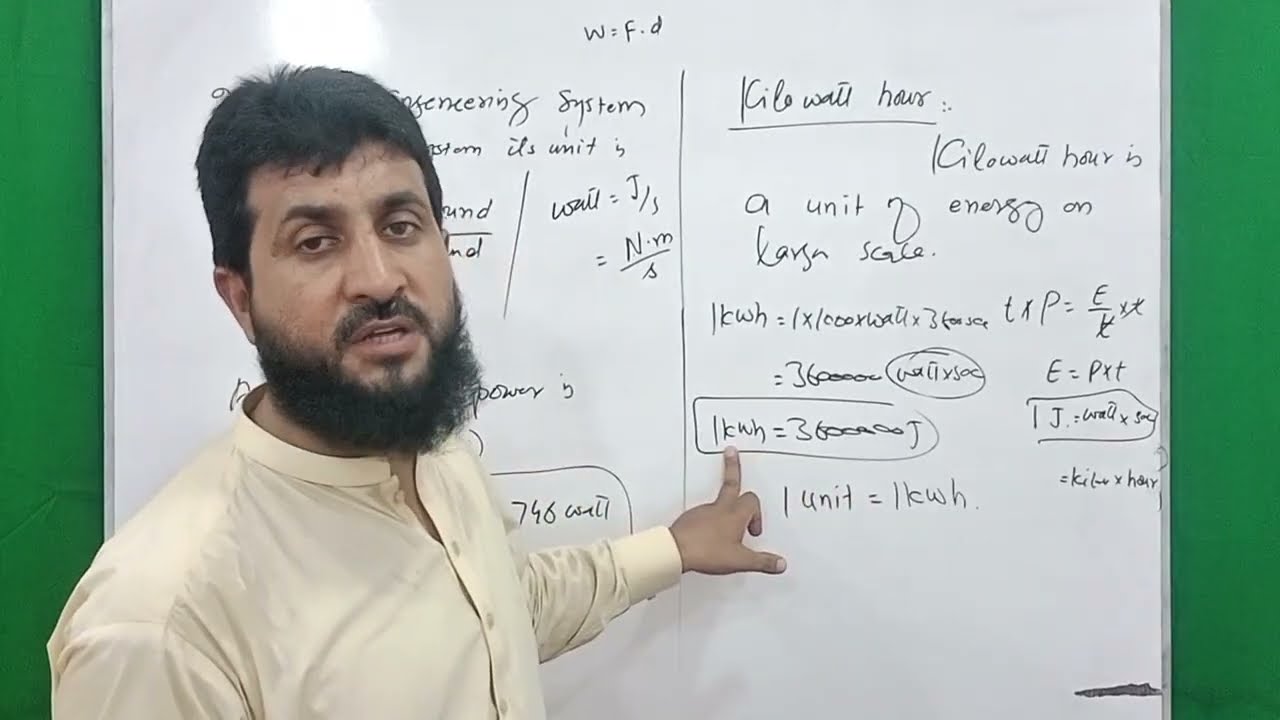
Definition: Power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred.
Units: The standard unit is the watt (W), where one watt equals one joule per second. Another common unit for engines is horsepower (hp).
Power is the amount of energy transferred or converted per unit time. In the International System of Units, the unit of power is the watt, equal to one joule per second. Power is a scalar quantity.
Specifying power in particular systems may require attention to other quantities; for example, the power involved in moving a ground vehicle is the product of the aerodynamic drag plus traction force on the wheels, and the velocity of the vehicle. The output power of a motor is the product of the torque that the motor generates and the angular velocity of its output shaft. Likewise, the power dissipated in an electrical element of a circuit is the product of the current flowing through the elem However, in systems where potential energy changes without explicit work being done (e.g., changing fields or conservative forces), the total energy definition is more general.
We will now show that the mechanical power generated by a force F on a body moving at the velocity v can be expressed as the product of force and velocity.
If a constant force F is applied throughout a distance x, the work done is
Units
The dimension of power is energy divided by time. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of power is the watt (W), which is equal to one joule per second. Other common and traditional measures are horsepower (hp), comparing to the power of a horse; one mechanical horsepower equals about 745.7 watts. Other units of power include ergs per second (erg/s), foot-pounds per minute, dBm, a logarithmic measure relative to a reference of 1 milliwatt, calories per hour, BTU per hour (BTU/h), and tons of refrigeration.
Average power and instantaneous power
As a simple example, burning one kilogram of coal releases more energy than detonating a kilogram of TNT,[6] but because the TNT reaction releases energy more quickly, it delivers more power than the coal. If ΔW is the amount of work performed during a period of time of duration Δt, the average power Pavg over that period is given by the formula.
For more amazing lectures please subscribe our channel.
For more lectures of class 9th visit link below
• class 9 physics chapter 1 physical quantit...
• Work and energy class 9 physics
• Gravitation class 9 physics
• Turning effect of forces class 9 physics
• class 9 physics chapter 3 dynamics
• class 9 physics chapter 2 Kinametics
For more lectures of class 10th visit link
• Physics Class 10th
For more lectures of class 11th visit link
• Physics Class 11
For more lectures of class 12th visit link
• Physics Class 12th
#lecturesofphysics #workandenergy #power #physics
#physics
#inter physics
#matric level physics
#school level physics
#fsc physics

Информация по комментариям в разработке