(USMLE topics) Structure of the skin, layers of the epidermis, skin barrier and pigmentation.
Purchase a license to download a non-watermarked version of this video on AlilaMedicalMedia(dot)com
Check out our new Alila Academy - AlilaAcademy(dot)com - complete video courses with quizzes, PDFs, and downloadable images.
Voice by: Ashley Fleming
©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved.
All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
The skin covers the body and protects it from the external environment. It also prevents water loss, provides sensory function, plays a role in body temperature regulation, and is the site of vitamin D synthesis.
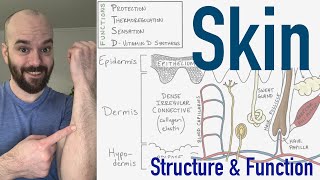
The skin is composed of 2 layers: the outer epidermis and the deeper dermis. The dermis is connected to underlying structures via a subcutaneous tissue, the hypodermis, which is not technically considered part of the skin.
The epidermis provides barrier and protection, it consists mainly of the protein keratin, a tough and water-insoluble structural protein.
The dermis constitutes the bulk of the skin, it provides support and flexibility. The dermis consists mainly of collagen, and to a lesser extent, elastin fibers. Loss of collagen and elastin, such as with aging, causes the skin to slack. The boundary surface between the epidermis and dermis is not flat but wavy, meaning the 2 tissues interlock, strengthening their connection. With age, this boundary flattens and the skin becomes more fragile. The dermis is well vascularized and contains sensory nerves, hair follicles, sebaceous glands and sweat glands. It has 2 zones: the upper papillary dermis with loose connective tissue, and the lower reticular dermis with denser connective tissue. The dermis houses immune cells and allows inflammatory response to activate upon exposure to invading organisms.
The hypodermis is composed of loose connective and adipose tissues. This is where most of the body fat is stored. The hypodermis provides thermal insulation, padding and serves as the body main energy storage.
The thickness and proportion of the epidermis and dermis vary greatly depending on their location on the body, but the skin is classified as thick or thin based on the thickness of the epidermis alone. Thick skin is found only in areas where there is a lot of abrasion: palms, soles, digits; and has 5 epidermal layers. Thin skin is everywhere else and has 4 epidermal layers.
Most cells of the epidermis are keratin-producing cells, or keratinocytes. New cells are constantly produced by mitotic cell division in the basal layer. They then move towards the skin surface as they age and differentiate, changing shape, from cuboidal to flat. The distinct epidermal layers represent different stages of keratinocyte differentiation, from their birth to their death.
The spinous layer is characterized by presence of abundant desmosomes which connect keratin filaments of adjacent cells, anchoring them together, providing resistance to physical stress.
The granular layer is loaded with keratohyalin granules. These granules release several substances that cross-link keratin filaments, converting them into an impermeable keratin matrix. This process is known as cornification or keratinization, the result of which is the most superficial layer, the cornified layer, about 30 cells thick. These fully keratinized dead cells form the skin barrier. They are shed periodically from the surface as new cells are moving up. The entire epidermis is replaced every 30 to 40 days. The renewal process becomes slower with age but faster in injured skin, when cell proliferation is accelerated for wound healing.
The epidermis also contains immune cells, touch sensory cells and melanocytes. Melanocytes produce the pigment melanin and transfer it to keratinocytes. The amount of melanin produced is the major determinant of skin color. Melanin synthesis is stimulated by UV light and is thought to be a protective mechanism against UV radiation damage.








Информация по комментариям в разработке