Learn how to seamlessly replace a database with a copy of another in SQL Server using straightforward steps and SQL queries in this comprehensive guide.
---
This video is based on the question https://stackoverflow.com/q/64054217/ asked by the user 'Joe' ( https://stackoverflow.com/u/190592/ ) and on the answer https://stackoverflow.com/a/64066213/ provided by the user 'Joe' ( https://stackoverflow.com/u/190592/ ) at 'Stack Overflow' website. Thanks to these great users and Stackexchange community for their contributions.
Visit these links for original content and any more details, such as alternate solutions, latest updates/developments on topic, comments, revision history etc. For example, the original title of the Question was: Replace Database WIth Copy Of Other Database
Also, Content (except music) licensed under CC BY-SA https://meta.stackexchange.com/help/l...
The original Question post is licensed under the 'CC BY-SA 4.0' ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/... ) license, and the original Answer post is licensed under the 'CC BY-SA 4.0' ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/... ) license.
If anything seems off to you, please feel free to write me at vlogize [AT] gmail [DOT] com.
---
How to Replace a Database with a Copy of Another Database in SQL Server
In the world of database management, there are times when you may want to replace one database with another, especially during testing or development phases. If you're managing SQL Server and need to automate the process of dropping a database, backing up another, and restoring it as the new database, you're in the right place. This guide will guide you step-by-step through this process, ensuring that you have a clean and efficient way to achieve your goals.
The Problem
Imagine you have two databases, DatabaseA and DatabaseB. For your testing process, you want to:
Drop DatabaseB: You need to remove an existing testing database.
Create a backup of DatabaseA: Before replacing anything, it’s wise to back up the database that you'll be copying from.
Recreate DatabaseB from the backup of DatabaseA: Finally, use that backup to restore DatabaseB.
While SQL Server offers some direct commands for performing these actions, the process requires careful execution to avoid any data loss or errors, especially if you have constraints on your server. Here’s how to accomplish this in a clean manner.
The Solution
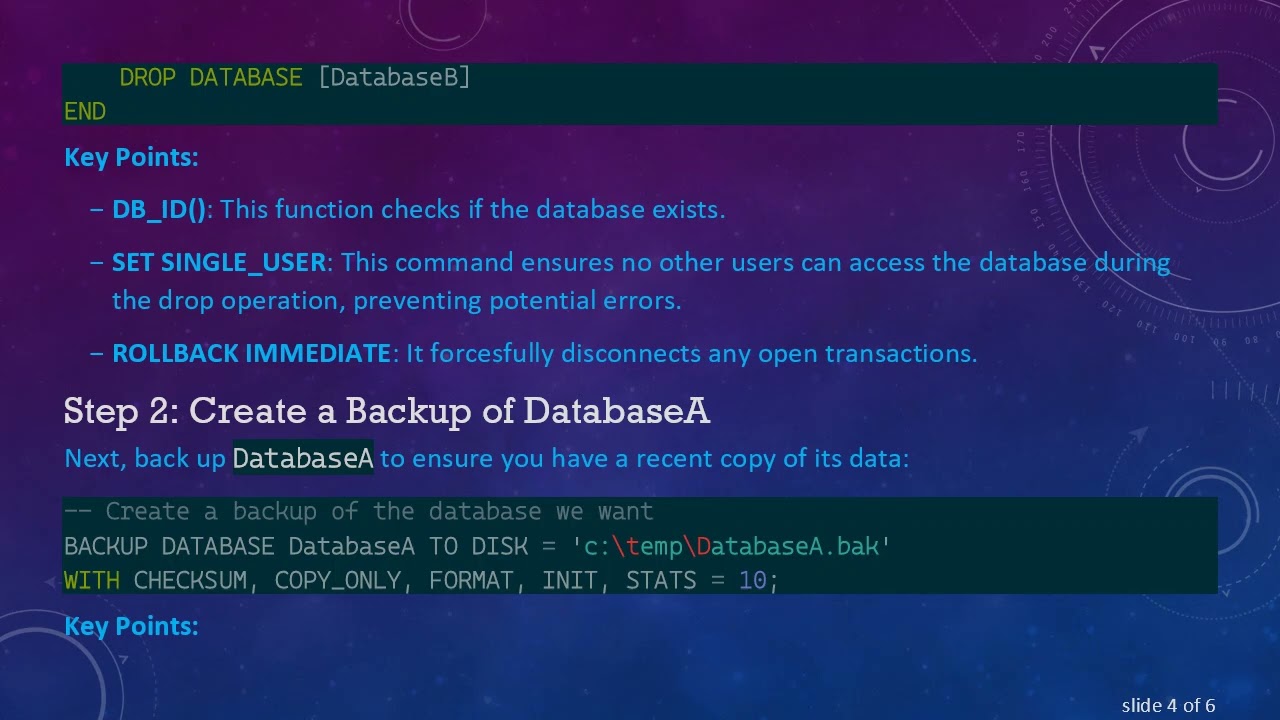
Step 1: Drop the Existing Database
To start, you need to drop DatabaseB. This involves setting the database to single-user mode and then dropping it. Here is how you can do it:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
Key Points:
DB_ID(): This function checks if the database exists.
SET SINGLE_USER: This command ensures no other users can access the database during the drop operation, preventing potential errors.
ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE: It forcesfully disconnects any open transactions.
Step 2: Create a Backup of DatabaseA
Next, back up DatabaseA to ensure you have a recent copy of its data:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
Key Points:
COPY_ONLY: This option ensures the backup won't interfere with the regular backup sequence of DatabaseA.
FORMAT, INIT: These options ensure that the backup is freshly created each time, without concatenating to any old backups.
Step 3: Restore the Backup to DatabaseB
Now that you have backed up DatabaseA, restore this backup to create DatabaseB:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
Key Points:
MOVE: This command directs SQL Server on where to place the new data and log files, avoiding conflicts with pre-existing database files.
RECOVERY: This option makes the database available again, allowing it to be used immediately after restoration.
Closing Thoughts
By following these steps, you can efficiently replace DatabaseB with a copy of DatabaseA, ensuring your testing environment is up-to-date and reflective of the current data in DatabaseA. The SQL commands provided not only streamline the process but also implement necessary precautions to protect your data.
Always remember to test these commands in a safe environment before executing them in your live systems to avoid unintended data loss.
With this guide, you're now equipped to handle the process of replacing databases in SQL Server with confidence!

Информация по комментариям в разработке