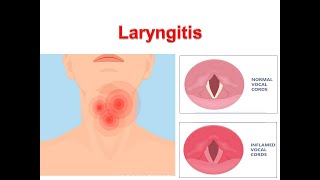
Laryngitis—inflammation of the larynx and surrounding structures.
The larynx, also known as the voice box, is a structure located at the top of the trachea and contains the vocal cords, two folds of tissue that vibrate to produce sound when we speak or sing.
When the larynx is inflamed, can lead to hoarseness, change in the sound of the voice, or loss of voice.
Symptoms:
The main symptom of laryngitis is hoarseness.
Breathy voice, sometimes progressing to a complete loss of voice.
It can be associated with dry cough and throat pain;
patients often feel a need to clear their throats.
Causes:
Viral infections
The most common cause of laryngitis is a viral infection, such as the common cold or flu. In children, the parainfluenza virus can cause croup, or laryngotracheobronchitis, which causes a “barking” cough.
Bacterial infection also can cause laryngitis, but usually, it is the complication of viral infection, occurring after 7 days of illness.
Overuse of the voice:
Using the voice excessively or improperly can lead to laryngitis. This is commonly seen in singers, actors, and other individuals who rely on their voices for their work, e.g., due to yelling, screaming, or loud singing.
Acid reflux:
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease, can cause laryngitis by causing acid from the stomach to flow back into the esophagus and irritate the larynx.
Fungal infection is rare but occurs in immunosuppressed patients or those treated with antibacterial medications.
Smokers are at elevated risk for malignancy and other infections.
Diagnosis is based on Symptoms, Indirect examination with a mirror or flexible laryngoscopy usually shows erythema and edema of the vocal cords and surrounding structures.
Treatment:
Laryngitis is generally self-limited, usually lasting 3–7 days, sometimes up to 2 weeks.
Vocal rest is crucial.
Airway humidification and hydration is important.
If laryngitis is caused by acid reflux, anti-reflux medication is recommended.
Generally, antibiotics aren’t effective in decreasing objective symptoms of laryngitis.
Red flags for emergency evaluation and monitoring include
Red flags include shortness of breath, stridor, dysphagia, and odynophagia.
A history of smoking or unexplained weight loss should raise suspicion of malignancy. Symptoms lasting more then 3 weeks should prompt referral to an otolaryngologist or speech specialist.
By MylesSG - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...
By Med Chaos - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...
By https://www.myupchar.com/en - https://www.myupchar.com/en/disease/h..., CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...









Информация по комментариям в разработке