👉📖 READY TO ACE YOUR EXAM? 📚 GET STUDY NOTES ON PATREON!
/ speedpharmacology
Antiarrhythmics are drugs that are used to treat abnormal rhythms of the heart, such as atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation. In general, antiarrhythmic drugs work by suppressing abnormal impulse formation, suppressing abnormal impulse conduction, or prolonging effective refractory periods. This pharmacology lecture covers topics such as cardiac conduction system: SA node, AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches, purkinje fibers, cardiac action potential, pacemaker cells, conducting cells, contractile cells; mechanisms of arrhythmias, bradycardia, tachycardia, abnormal automaticity, triggered activity, Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome, atrioventricular nodal reentry tachycardia, Vaughan-Williams classification, class I (A, B, C), class II, class III, class IV antiarrhythmic drugs. Antiarrhythmics mentioned include: Procainamide, Quinidine, Disopyramide, Lidocaine, Mexiletine, Flecainide, Propafenone, Propranolol, Metoprolol, Atenolol, Esmolol, Amiodarone, Dronedarone, Sotalol, Dofetilide, Ibutilide, Verapamil, Diltiazem, Digoxin, Adenosine, and Magnesium Sulfate.
Thanks for watching and don't forget to SUBSCRIBE, hit the LIKE button👍 and click the BELL button🔔 for future notifications!!!
Source of the animation of the cardiac conducting system: http://www.passmyexams.co.uk/GCSE/bio...
0:00 Intro - Basics of ECG
1:55 Cardiac cell types
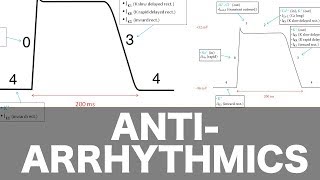
3:40 Pacemaker potential
5:16 Cardiac muscle cell potential
7:09 Types of arrhythmia
12:08 Class I antiarrhythmics
15:26 Class II antiarrhythmics
16:39 Class III antiarrhythmics
18:52 Class IV antiarrhythmics
19:45 Digoxin,
21:51 Adenosine
22:38 Magnesium









Информация по комментариям в разработке