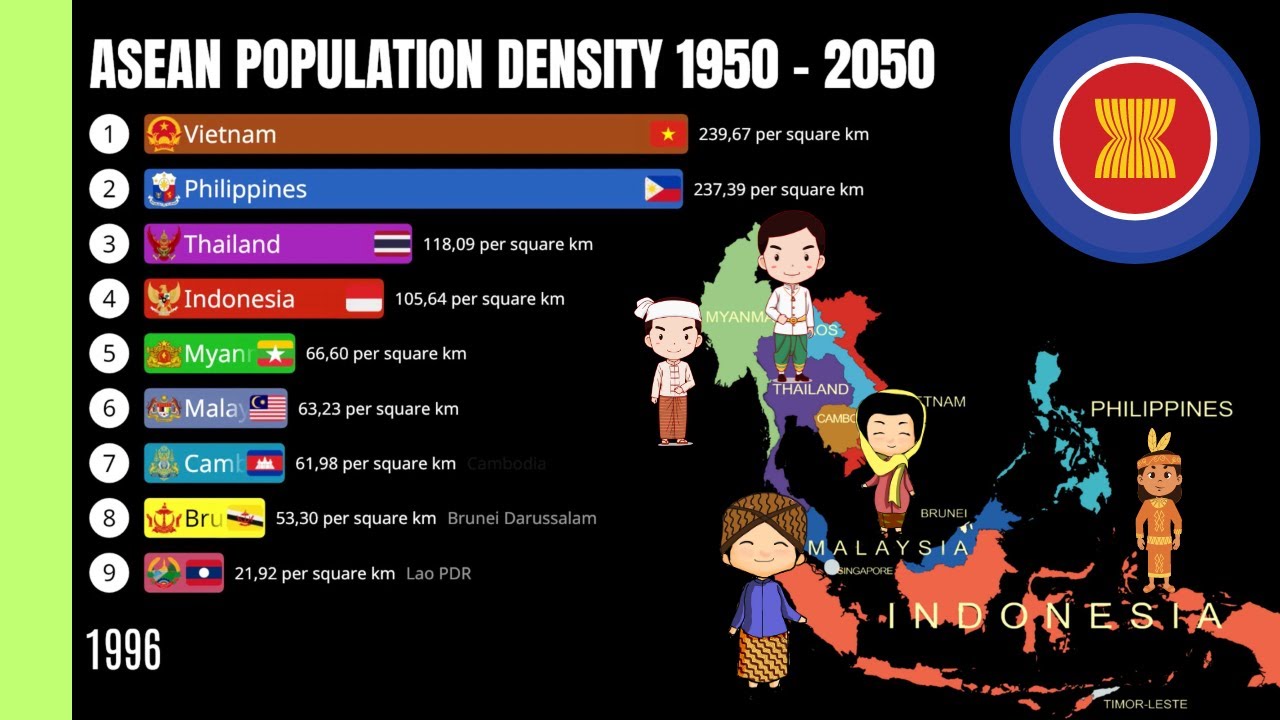
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is a regional organization comprising ten member countries in Southeast Asia. With a combined population of over 650 million people, ASEAN is one of the most populous regions in the world. Population density, which refers to the number of people per unit area, varies significantly across ASEAN member countries due to various factors such as geographical features, urbanization, economic development, and historical trends.
Geographical features play a crucial role in shaping population density within ASEAN. The region consists of diverse landscapes, including islands, mountains, coastal areas, and river deltas. Countries such as Indonesia and the Philippines, which are archipelagos, exhibit variations in population density due to the presence of multiple islands. Coastal areas and river deltas often have higher population densities as they provide access to transportation, trade routes, and fertile land for agriculture. For example, the densely populated island of Java in Indonesia is known for its rich agricultural resources and historical significance as a political and economic center.
Urbanization is another key factor influencing population density in ASEAN. The region has experienced rapid urbanization in recent decades, as people migrate from rural areas to cities in search of better employment opportunities, education, and improved living conditions. Countries such as Singapore, Malaysia, and Thailand have witnessed significant urbanization, resulting in densely populated cities and urban centers. The growth of industries, services, and infrastructure in these urban areas has attracted a large influx of people, leading to increased population density.
Economic development and employment opportunities also contribute to population density variations in ASEAN. Countries with robust economies and strong job markets often attract internal and international migration, leading to population concentration in certain regions. Thailand's economic growth and industrial development, for instance, have resulted in higher population densities in the central regions, particularly around the capital city of Bangkok. Similarly, countries like Malaysia and Singapore have drawn large numbers of foreign workers, contributing to population density in specific areas.
Historical factors and demographic trends also influence population density within ASEAN. Some regions have traditionally been more populated due to historical settlements or cultural factors. For example, areas surrounding ancient capitals or centers of trade tend to have higher population densities. On the other hand, regions affected by conflicts or political instability may experience lower population densities due to displacement or migration. Historical events such as colonialism and the movement of people during and after World War II have also shaped population density patterns in the region.
The population density in ASEAN has significant implications for the member countries. High population density in urban areas poses challenges in terms of urban planning, infrastructure development, and the provision of public services. Congestion, housing shortages, strain on transportation systems, and increased demand for energy and water resources are common issues faced by densely populated cities. Governments need to invest in adequate infrastructure, housing, healthcare facilities, educational institutions, and social welfare services to cater to the needs of a growing population.
Conversely, low population density in certain areas presents its own set of challenges. Remote regions may face difficulties in accessing basic services, healthcare, education, and economic opportunities. The development gap between densely populated urban centers and sparsely populated rural areas can lead to social and economic disparities. Governments must implement policies and initiatives to promote balanced regional development, improve connectivity, and provide incentives for investment in rural areas to address these disparities.
ASEAN, ASEAN Population, ASEAN Population Density, Indonesia, Indonesia Population, Vietnam, Vietnam Population, Thailand, Thailand Population, Philippines, Philippines Population, Cambodia, Cambodia Population, Indonesia Population Density, Vietnam Population Density, Philippines Population Density, Malaysia Population, Malaysia Population Density, Southeast Asia

Информация по комментариям в разработке