Gene Cloning Animation | Genetic Engineering | Basic Science Series
Keywords: Gene cloning, molecular cloning, DNA cloning, recombinant DNA, gene manipulation, biotechnology, genetic engineering, PCR amplification, gene isolation, plasmid vectors, DNA ligase, transformation process, selective markers, antibiotic resistance genes, PCR screening, DNA sequencing, biomedical research, disease mechanisms, therapeutic targets, genetic modification, crop improvement, disease-resistant plants, pharmaceutical production, forensic DNA analysis, environmental monitoring.
Gene cloning is a revolutionary technique in molecular biology that allows scientists to replicate and manipulate specific genes for various purposes. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of gene cloning, from its fundamental principles to its applications in research, medicine, and biotechnology.
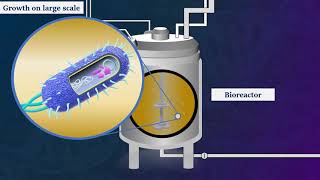
Gene cloning, also known as molecular cloning, is the process of isolating and making copies of a specific gene or DNA sequence. This technique involves inserting the gene of interest into a vector, such as a plasmid or a viral genome, and then introducing the vector into a host organism, typically a bacterium or yeast. Once inside the host, the vector replicates along with the host's DNA, producing multiple copies of the inserted gene.
How Does Gene Cloning Work?
Gene cloning involves several key steps:
1. Isolation of the gene of interest: The target gene is identified and isolated from the source organism's DNA using techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or restriction enzyme digestion.
2. Preparation of the vector: A vector, usually a circular DNA molecule such as a plasmid, is prepared by cleaving it with the same restriction enzymes used to isolate the gene. This creates compatible sticky ends that allow the gene to be inserted into the vector.
3. Insertion of the gene into the vector: The isolated gene is ligated into the vector using DNA ligase, forming a recombinant DNA molecule.
4. Transformation: The recombinant DNA molecule is introduced into a host organism, such as bacteria or yeast, through a process called transformation. The host organism takes up the recombinant DNA and replicates it along with its own DNA.
5. Selection and screening: Selective markers, such as antibiotic resistance genes, are often incorporated into the vector to identify host cells that have successfully taken up the recombinant DNA. Screening techniques, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or DNA sequencing, are used to verify the presence of the desired gene in the host cells.
Applications of Gene Cloning:
Gene cloning has a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
1. Biomedical research: Gene cloning is used to study the function of specific genes and their role in diseases, leading to insights into disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets.
2. Genetic engineering: Gene cloning allows scientists to modify organisms for various purposes, such as enhancing crop yield, developing disease-resistant plants, or producing pharmaceuticals and vaccines.
3. Forensic science: Gene cloning techniques are employed in DNA fingerprinting and forensic analysis to identify individuals based on their unique genetic profiles.
4. Environmental monitoring: Gene cloning is used to detect and monitor environmental pollutants, pathogens, and other microorganisms in air, water, and soil samples.
WhatsApp group: https://chat.whatsapp.com/HTXQC1Ax2qf...
Twitter: / basic_series
Facebook Group: / 742235929758671
LinkedIn: / basic-science-series-a54439208
Instagram: / basic_science_series
Support my work at https://www.patreon.com/user?u=37177596
Disclaimer: The information provided is for educational purposes only. The content of this channel should not be considered as medical advice of any kind. Use this information at your own risk. We hold no responsibility for any issue, concerns, or damage arising from the content of the video. Under no circumstances this channel be responsible or liable in any way for any content, including but not limited to, any errors or omissions in the content, any loss, any damage of any kind incurred as a result of any content communicated in this video, whether by this channel or a third party. In no event shall this channel be liable for any special indirect or consequential damages of any damages whatsoever resulting from the content of the channel.








Информация по комментариям в разработке