Decoding the Hidden World of Metagenomics and Strain Profiling🌐 [Advancements in Microbial Research The Shift from Traditional Culturing to Metagenomics🌐📊💻] Understanding Microbial Interactions in Computational Metagenomics🌱🌐
Advancing Microbial Research: From Isolated Culturing to Comprehensive Metagenomic Insights on Microbial Communities.
Understanding Beta Diversity and Metagenomic Analysis🌱📊📚
[00:04]( • Видео ) Traditional microbiology's reliance on pure cultures limits understanding of microbial diversity.
The classical approach involved isolating and growing microbes in lab settings, often leading to incomplete insights.
Many microbes cannot be cultured under lab conditions, resulting in a significant portion of microbial life remaining uncharacterized.
[00:45]( • Видео ) Non-culturability of microbes limits traditional research methods.
Over 99% of microbes cannot be cultured using standard laboratory techniques, leading to gaps in research.
Culturing microbes outside their natural environment removes crucial ecological interactions that influence their behavior and function.
[01:22]( • Видео ) Metagenomics captures ecosystem interdependencies by analyzing environmental DNA directly.
Studying isolated organisms fails to reveal crucial ecological interactions and resilience mechanisms.
Metagenomics offers a holistic view by sequencing DNA from diverse environments, preserving ecological snapshots.
[02:01]( • Видео ) Metagenomics reveals interdependencies in microbial communities beyond individual species.
Traditional genomics focuses on single species, limiting understanding of their ecological roles.
Metagenomics allows for bulk sequencing, capturing the collective genetic information of diverse organisms in a community.
[02:38]( • Видео ) Metagenomics reveals microbial diversity and functional capabilities in ecosystems.
In soil metagenomes, various species encode specific enzymes, contributing to ecological functions like cellulose degradation and nitrogen fixation.
The microbiome encompasses not just the microorganisms but also their genomic content and functional potential, offering insights into ecological interactions.
[03:15]( • Видео ) Pang genomes reveal extensive genetic diversity within microbial species.
The pang genome encompasses all genes from different strains, showcasing functional diversity within a single species.
It is divided into the core genome, which includes essential genes shared by all strains, and the accessory genome, containing strain-specific genes for adaptations and resistance.
[03:54]( • Видео ) Strain-level profiling guides precision medicine and ecological studies.
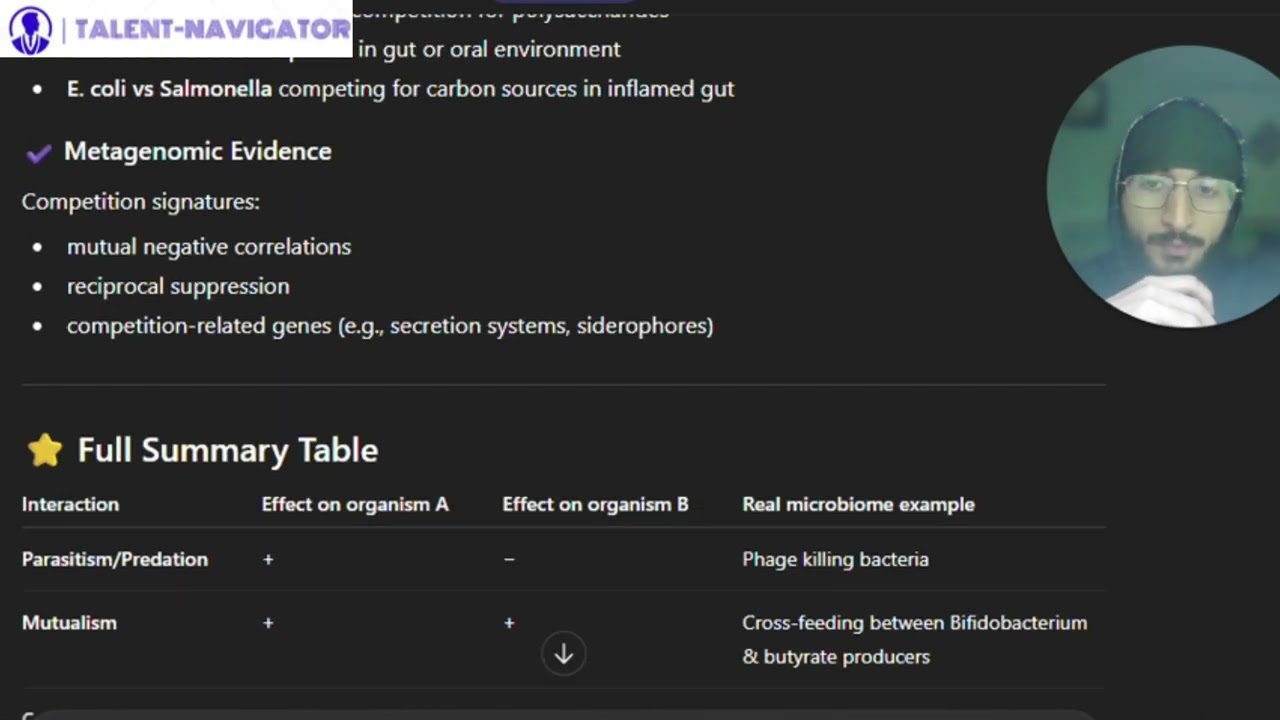
E.coli strains share less than 50% of genes, highlighting the importance of understanding genetic diversity.
Metagenomics faces challenges in identifying community composition, utilizing algorithms for taxonomic classification.
[04:32]( • Видео ) Metagenomics uncovers previously unknown microbial diversity and novel organisms.
Metagenomics allows the discovery of novel candidate phyla and ultra-small bacteria that traditional culturing cannot identify.
Recent findings include giant viruses like the mimi virus and Pandora virus, highlighting the limitations of current microbial databases.
metagenomics,microbial diversity,microbiome research,environmental DNA,pang genome,core genome,accessory genome,microbial genomics,precision medicine,ecological genomics,soil metagenomics,microbial ecology,microbiome studies,nonculturable microbes,microbial community,bulk sequencing,taxonomic classification,microbial interdependencies,ecosystem genomics,giant viruses,e coli strains,cellulose degradation,pandora virus,mimivirus,genomics,bioinformatics

Информация по комментариям в разработке