Welcome to Lecture 6️⃣ of Class 12 Biology – Agents of Pollination, Floral Adaptations & Outbreeding Devices, taught by Meenakshi Ma’am at B2E Learning.
This lecture is a continuation of the Pollination chapter from Reproduction in Flowering Plants, one of the most important segments of NEET Botany. This session covers detailed concepts that help students understand how different flowers evolve special strategies to achieve effective pollination and ensure genetic diversity.
We begin with a highly detailed explanation of Agents of Pollination—both abiotic and biotic.
Abiotic agents include:
🌬️ Wind Pollination (Anemophily): Features of wind-pollinated flowers like reduced perianth, dry pollen, feathery stigma, large pollen quantity, and typical examples such as maize, grass, wheat, sugarcane.
💧 Water Pollination (Hydrophily): Characteristic features in submerged plants, surface vs underwater pollination, and examples like Vallisneria and Hydrilla.
Biotic agents include:
🐝 Insects (Entomophily): Bright coloured petals, nectar guides, fragrance, nectar secretion, edible pollen, and mutualistic interactions.
🐦 Birds (Ornithophily) and 🦇 Bats (Chiropterophily): Adaptations like large sturdy flowers, abundant nectar, tubular corolla, nighttime blooming, and specific examples from NCERT.
Each agent is described with important adaptations, examples, mechanisms, and differences between abiotic and biotic pollination, all with NEET-relevant facts.
Next, the lecture discusses Floral Adaptations, focusing on structural, behavioral, and ecological strategies that flowers use to maximize pollination chances. Topics include stigma structure, pollen production strategies, nectar formation, flower orientation, colour change, and unique cases of mimicry (e.g., Ophrys flower). All adaptations are explained with NCERT diagrams and simplified illustrations for easy retention.
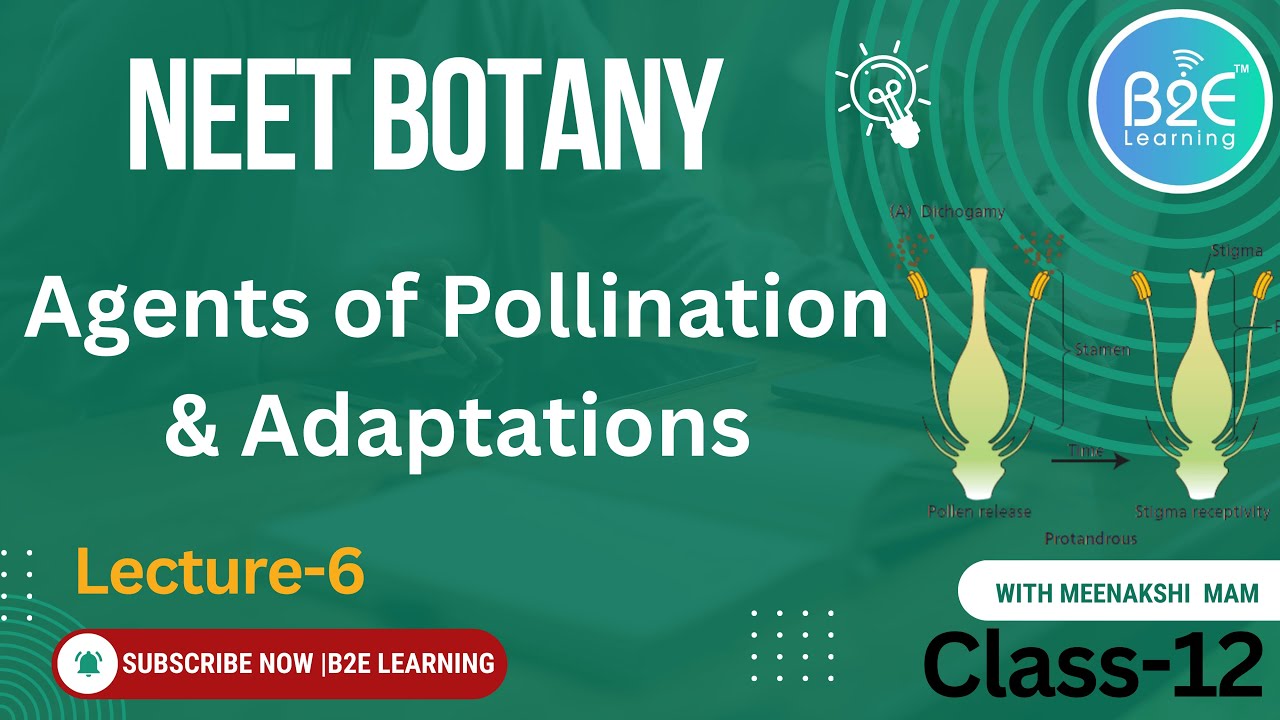
The session also covers Outbreeding Devices, the most crucial part of this lecture. These are evolutionary mechanisms developed by plants to prevent inbreeding and promote cross-pollination for maintaining genetic diversity.
The lecture explains:
🔸 Dichogamy – Protogyny & Protandry
🔸 Herkogamy – Physical barriers preventing self-pollination
🔸 Self-Incompatibility – Genetic mechanisms that avoid self-fertilization
🔸 Heterostyly & Heteromorphy
🔸 Male & Female flower separation (Monoecy & Dioecy)
Each concept is supported with definitions, diagrams, examples, advantages, and NEET pointers.
This lecture also includes:
✔️ Complete NCERT line-by-line integration
✔️ Previous Year NEET MCQs
✔️ Expected questions targeting 2025 NEET exam
✔️ Short tricks & memory aids
✔️ Summary of each concept for last-minute revision
Perfect for Class 12 students, NEET UG aspirants, droppers, and anyone preparing for medical entrance exams.
With B2E Learning and Meenakshi Ma’am’s simple explanations, chapter flow, and deep conceptual teaching, students can master the Pollination chapter and improve exam accuracy significantly.
#Lecture6 #6️⃣Lecture6 #AgentsOfPollination #PollinationClass12 #NEETBiology #NEET2025 #NEETUG #B2ELearning #Class12Biology #MeenakshiMam #ReproductionInFloweringPlants #BotanyNEET #NCERTBiology #WindPollination #Anemophily #Hydrophily #WaterPollination #Entomophily #InsectPollination #BirdPollination #Ornithophily #BatPollination #Chiropterophily #BioticPollination #AbioticPollination #FloralAdaptations #PollinationAdaptations #OutbreedingDevices #Dichogamy #Protandry #Protogyny #Herkogamy #SelfIncompatibility #Heterostyly #MonoeciousPlants #DioeciousPlants #NCERTLineByLine #NEETBotany #BiologyLecture #MedicalAspirants #NEETDropper #NEETTarget2025 #CBSEBiology #NCERTConcepts #BiologyRevision #ExamOrientedLecture #ScoreFullMarks #PlantReproduction

Информация по комментариям в разработке