(USMLE topics) Principles of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis, pros and cons.
Purchase a license to download a non-watermarked version of this video on AlilaMedicalMedia(dot)com
Check out our new Alila Academy - AlilaAcademy(dot)com - complete video courses with quizzes, PDFs, and downloadable images.
Voice by: Ashley Fleming
©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved.
All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Dialysis is a therapy that artificially removes wastes from the blood of patients whose kidneys can no longer perform this function adequately. There are two main types of dialysis: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
In hemodialysis, blood is filtered outside the body, in a dialysis machine. The patient’s blood is pumped to the machine, cleansed, then returned to the body. To prepare for regular hemodialysis treatments, a one-time minor surgery is performed to create a vascular access, which is essentially a large and strong vein, enough to sustain the high flow rate through the machine. This can be accomplished by fusing an artery to a vein, forming a fistula; or by adding a graft. For emergency treatment, a catheter can be used for temporary access.
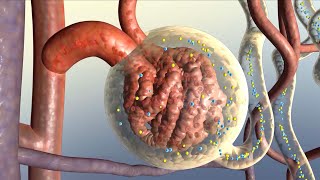
Once inside the machine, blood flows within tiny tubes surrounded by a dialysis solution, called dialysate. The walls of the tubes act as semipermeable membranes that allow only small molecules, such as water, nitrogenous wastes and electrolytes, to pass through. The filtration occurs by osmosis and diffusion, where water and solutes move from higher to lower concentration. The dialysis fluid contains solutes at the levels similar to those in healthy blood. Urea, potassium and other solutes that are present at higher levels in patient’s blood, move out to the dialysate, which is constantly replaced and discarded. At the same time, other substances can be added to the dialysis fluid to be administered to the patient. These may include: bicarbonate, to adjust the patient’s blood pH; erythropoietin, to compensate for its low production by the failing kidneys; and certain medications. Because of the increased risks of blood clotting associated with its contact with foreign surfaces, an anticoagulant such as heparin is usually added. The composition of dialysis fluid is typically prescribed by a nephrologist based on the patient’s needs.
Hemodialysis frequency of treatment: 4-hour treatments, 3 times a week, in a dialysis center. Complications: risks of blood infection, thrombosis, internal bleeding due to the added anticoagulant.
In peritoneal dialysis, the dialysis fluid is introduced into the patient’s abdominal cavity via a catheter. The lining of the abdomen, the peritoneum, serves as the natural filtering membrane. The fluid remains in the body for several hours, allowing exchange and equilibrium with the blood running in the underlying vessels, before being discarded. The therapy can also be done automatically at night during sleep.
Peritoneal dialysis is less effective than hemodialysis, but because it can be performed for longer periods of time, the result is comparable. Peritoneal dialysis advantages: more flexibility, is better tolerated by patients, and less expensive; disadvantages: more often complicated with abdominal infections.







Информация по комментариям в разработке