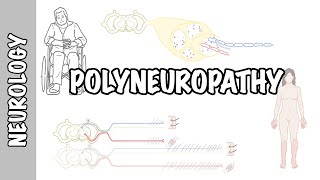
Toxic neuropathy refers to damage or dysfunction of the peripheral nerves caused by exposure to certain toxic substances. Peripheral nerves are responsible for transmitting signals between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body, controlling sensations and motor functions. When these nerves are damaged by toxins, it can result in a range of symptoms and complications.
Causes: Toxic neuropathy can be caused by various substances, including:
Chemical Agents: Exposure to certain industrial chemicals, heavy metals (such as lead, mercury, and arsenic), and solvents can lead to nerve damage.
Medications: Some drugs, especially those used in chemotherapy or certain antibiotics, can cause peripheral nerve damage as a side effect.
Alcohol: Chronic excessive alcohol consumption can result in alcoholic neuropathy, damaging peripheral nerves.
Environmental Toxins: Pesticides, herbicides, and other environmental toxins may contribute to neuropathy.
Industrial Agents: Workers in industries with exposure to chemicals, metals, and other harmful agents may be at risk.
Symptoms: Toxic neuropathy can manifest in various ways, including:
Numbness or tingling in extremities (hands, feet)
Muscle weakness or loss of coordination
Pain, often described as burning or stabbing
Sensitivity to touch or temperature changes
Difficulty with balance and walking
Muscle cramps or spasms
Autonomic symptoms like changes in blood pressure, heart rate, and digestion.
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, nerve function tests (such as electromyography and nerve conduction studies), and identifying potential exposure to toxins.
Treatment: Treating toxic neuropathy primarily involves:
Removing or Avoiding Toxins: Identifying and eliminating exposure to the causative toxic substances.
Symptomatic Relief: Managing pain, discomfort, and other symptoms through medications such as pain relievers, antidepressants, or anticonvulsants.
Physical Therapy: Improving muscle strength, coordination, and balance through exercises.
Supportive Care: Addressing complications like infections, ulcers, or injuries resulting from reduced sensation.
Prognosis: The outlook depends on the extent of nerve damage and the effectiveness of toxin avoidance and symptom management. Some cases can lead to significant disability, while others may show improvement over time.
Prevention: Preventive measures include proper handling of chemicals, following safety guidelines, using protective gear in workplaces, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and promptly addressing exposure to environmental toxins.
In essence, toxic neuropathy underscores the importance of recognizing and mitigating exposure to toxic substances to prevent or minimize nerve damage and its associated effects on overall health and well-being.
#ToxicNeuropathy #NerveDamage #PeripheralNeuropathy #Neurotoxicity #ToxinExposure
#ChemicalExposure #IndustrialToxins #NeuropathyAwareness
#NeurologicalHealth #HealthAwareness #ToxicSubstances
#NeuropathySupport #ToxinPrevention #NeuropathySymptoms #Neurology
#EnvironmentalHealth #ToxicityEffects #ChemicalSafety #NerveHealth #ToxinAwareness








Информация по комментариям в разработке