Learn how to effectively access sequence indices of aligned regions in `BioAlignments.jl` using Julia, allowing for better insight into DNA sequence alignments.
---
This video is based on the question https://stackoverflow.com/q/63991548/ asked by the user 'Entangler' ( https://stackoverflow.com/u/7210206/ ) and on the answer https://stackoverflow.com/a/63992533/ provided by the user 'Przemyslaw Szufel' ( https://stackoverflow.com/u/9957710/ ) at 'Stack Overflow' website. Thanks to these great users and Stackexchange community for their contributions.
Visit these links for original content and any more details, such as alternate solutions, latest updates/developments on topic, comments, revision history etc. For example, the original title of the Question was: How do I retrieve the sequence indices of an aligned region from a BioAlignments.jl alignment?
Also, Content (except music) licensed under CC BY-SA https://meta.stackexchange.com/help/l...
The original Question post is licensed under the 'CC BY-SA 4.0' ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/... ) license, and the original Answer post is licensed under the 'CC BY-SA 4.0' ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/... ) license.
If anything seems off to you, please feel free to write me at vlogize [AT] gmail [DOT] com.
---
Understanding Sequence Indices in BioAlignments.jl
If you're working in the bioinformatics field using Julia, you might encounter situations where you need to retrieve sequence indices of specific aligned regions from an alignment object created with BioAlignments.jl. This is particularly relevant when you're analyzing how sequences align relative to their original forms.
The Challenge
You might want to know where in your original sequences the alignment has occurred. For example, after using the pairalign function for alignment, you want to access the corresponding indices to understand the context of that alignment in the source sequences. Unfortunately, finding this information through documentation can be challenging. Let's explore how you can efficiently tackle this problem.
Accessing The Indices of Aligned Regions
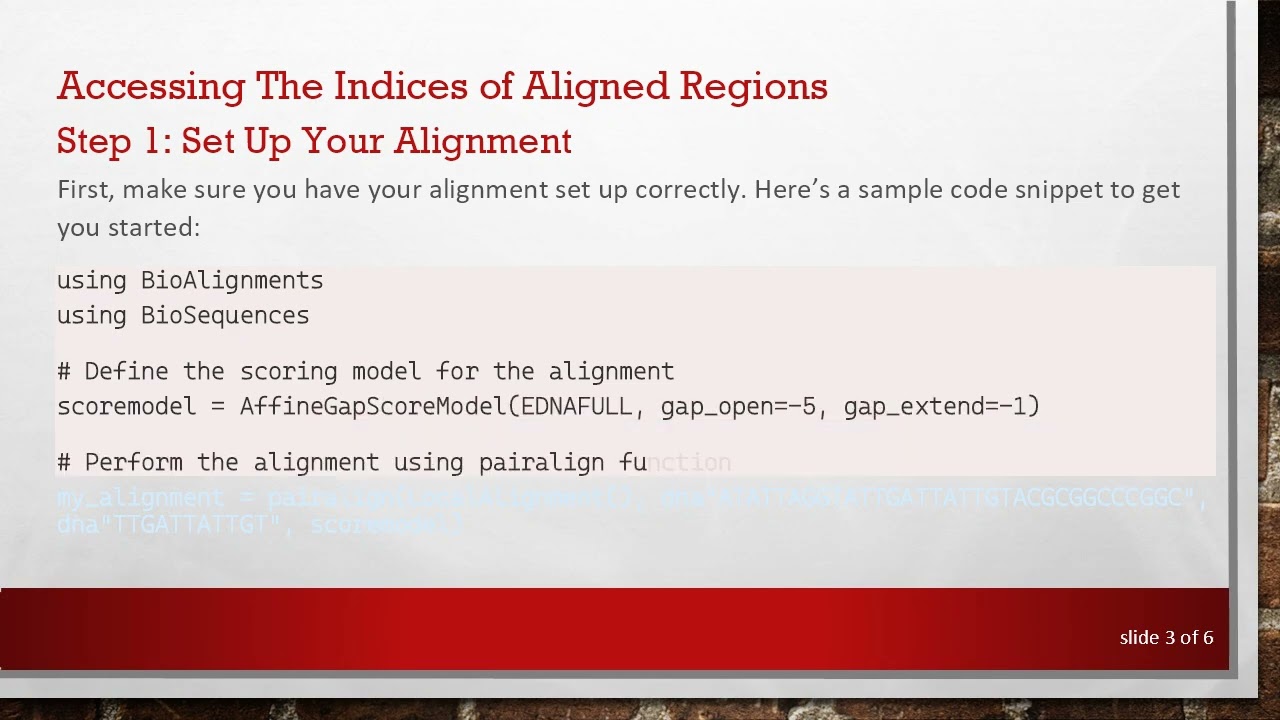
Step 1: Set Up Your Alignment
First, make sure you have your alignment set up correctly. Here’s a sample code snippet to get you started:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
Step 2: Examine the Alignment Object
To get the indices of the aligned regions, you can utilize the dump function on the alignment object. This method allows you to visualize the internal structure of the alignment, exposing valuable data points.
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
This command provides a comprehensive view of the data structure, indicating where specific information, such as sequence positions, is stored.
Step 3: Locate Index Information
After dumping the alignment object, focus on the anchors associated with the alignment. This holds the key to finding the indices you need:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
The output will show you an array of AlignmentAnchor objects, each representing a matched position in the original sequences. For example, you might see something like:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
Here, each AlignmentAnchor comprises:
seqpos: The position in the query sequence.
refpos: The position in the reference sequence.
op: The operation performed, indicating whether it's a start, match, or other operation.
Important Considerations
While using the dump function is effective for retrieving indices, it's important to keep in mind:
Library Changes: The data structures you are working with are not guaranteed to remain unchanged. Future updates to BioAlignments.jl could modify the internal formats or available fields. Always check the latest documentation.
Alternative Methods: As the library evolves, ensure you’re on the lookout for specific functions that may be introduced to simplify access to indices directly, avoiding the need for object dumping.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of alignment objects in BioAlignments.jl can seem daunting at first, especially when it comes to retrieving key sequence indices. However, with the outlined approach, you can effectively derive this important information for your bioinformatics tasks. Happy coding, and may your sequence alignments yield great insights!

Информация по комментариям в разработке