Learn how to effectively define a `ManyToMany` relationship among multiple entities in Hibernate, focusing on restaurant, kitchen, and dish models.
---
This video is based on the question https://stackoverflow.com/q/63412893/ asked by the user 'morj' ( https://stackoverflow.com/u/12275130/ ) and on the answer https://stackoverflow.com/a/63413026/ provided by the user 'Sudoss' ( https://stackoverflow.com/u/8938332/ ) at 'Stack Overflow' website. Thanks to these great users and Stackexchange community for their contributions.
Visit these links for original content and any more details, such as alternate solutions, latest updates/developments on topic, comments, revision history etc. For example, the original title of the Question was: @ ManyToMany Relationship Between Tables
Also, Content (except music) licensed under CC BY-SA https://meta.stackexchange.com/help/l...
The original Question post is licensed under the 'CC BY-SA 4.0' ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/... ) license, and the original Answer post is licensed under the 'CC BY-SA 4.0' ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/... ) license.
If anything seems off to you, please feel free to write me at vlogize [AT] gmail [DOT] com.
---
Understanding the ManyToMany Relationship in Hibernate
In the world of database management, establishing relationships between tables is crucial for efficient data handling. One of the most common types of relationships is the ManyToMany relationship, which allows for each record in one table (entity) to relate to multiple records in another table (entity) and vice versa. This guide will delve into how to define a ManyToMany relationship between three entities: Dish, Kitchen, and Restaurant using Hibernate.
The Problem
Suppose you have three separate entities:
Dish
Kitchen
Restaurant
You need to link these three entities effectively in a relational database using Hibernate. The question arises: How can you define this relationship in your entity classes? Additionally, is it necessary to create an intermediary table, often referred to as the Many model?
Understanding Your Entities
Before diving into solutions, let's get acquainted with our entities. Here’s a brief overview based on common attributes:
Kitchen Model
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
Dish Model
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
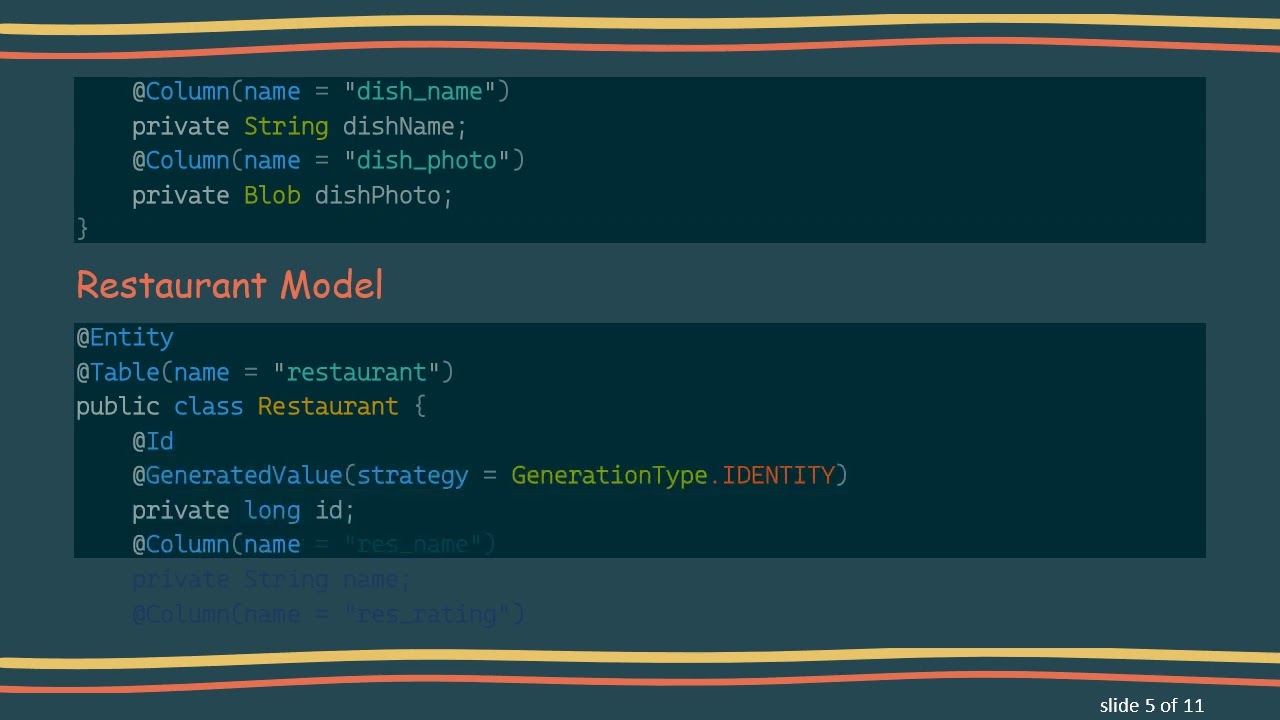
Restaurant Model
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
Linking Table - Many Model
This is an intermediary linking table where you might define relationships:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
The Solution: Defining Relationships
Understanding how restaurant, kitchen, and dish interact is vital. In this scenario, a Restaurant can have many dishes and is linked to one Kitchen. Here’s how to define these relationships:
Defining Relationships in Restaurant
In the Restaurant class, you can use @ OneToMany and @ OneToOne annotations to define the relationships:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
Defining Relationships in Dish
In the Dish class, you also need to indicate the relationship from the Dish side towards Restaurant:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
Defining Relationships in Kitchen
Similarly, if needed, you can define the relationship from the Kitchen side:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
Conclusion
In this approach, you effectively establish a ManyToMany relationship among the three entities without necessarily needing an intermediary model like Many. Instead, you define each relationship directly within the entity classes. The models establish clear, manageable links that facilitate data manipulation and retrieval. Ultimately, if your requirements don’t necessitate complex linking or additional attributes in the Many model, you can streamline the design by managing relationships directly among the primary entities.
By following this structured method, not only can you maintain clear relationships within your database, but you also gain flexibility as your application evolves.

Информация по комментариям в разработке