🎥 In the realm of 24-Volt DC sensors, it is inevitable to come across the term PNP, as it is a common and often confusing term used in the industry.
By watching this video, you’ll get the answer to these questions:
- What is a PNP sensor?
- How to test a PNP sensor?
- How to wire a PNP sensor?
- What is a PNP output sensor?
- How does a PNP sensor work?
- What is a PNP sensor used for?
- How to connect a PNP sensor to a PLC?
- What are the components of a PNP sensor?
- What are some common applications of PNP sensors?
======================================================
💬 Video Summary:
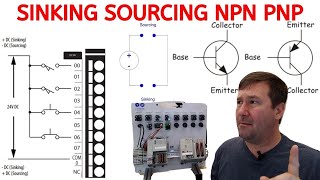
PNP Circuit
- First, you should learn whether the circuit is designed for PNP sensors.
- The PNP is shorthand for positive-negative-positive. The letter N in the middle of PNP, short for Negative polarity, reminds you that the load should be connected directly to the Negative side of the power supply.
PNP Sensor Diagram
- Let's take a closer look at the internal circuit design of a 3-wire PNP sensor. Generally, it consists of a sensing element circuitry and a PNP transistor.
PNP Sensor Wiring
- Solid-state 3-Wire PNP sensors are classified as active devices and typically need a small amount of operating power.
- The brown wire of the PNP sensor, known as the power wire, is attached to the positive side of the power supply, and then the blue wire of the PNP sensor is connected to the power supply's negative terminal.
- The third wire of the PNP sensor, which is black, is identified as the signal output wire of the sensor that is going to connect to the input terminal of the load.
PNP Sensor Working
- Whenever the PNP sensor doesn't detect any metal object, the active line is low. Thus, the PNP transistor is off and behaves somewhat as an open switch. As a result, no current flows in or out of the PNP output, and the light bulb is off.
- But detecting a metal object by the PNP sensor makes the active line goes high and subsequently turns the PNP transistor on to act somewhat as a closed switch. As a result, it enables the flow of current from the power supply's positive terminal, through the PNP transistor, towards the PNP sensor output and eventually to the negative terminal of the power supply via the load.
- So, the function of the PNP sensor in providing power to the load is why it is commonly known as the sourcing sensor.
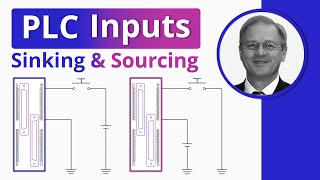
PNP Sensor Connection to PLC
- The type of field sensor used in the industry must be complementary to the PLC discrete input module type. Since you put the PNP or sourcing sensor here, you need a sinking PLC discrete input module to go along with it.
- Connect the black wire of the PNP sensor, which represents the PNP sensor output, to the input of the PLC module, and the power supply's negative terminal should be connected to the PLC module's common terminal.
Checking PNP Sensor
- Finally, let's learn how to test the PNP sensor to see if it works correctly. To do so, you need to get your multimeter into play.
- Connect the red lead of the multimeter to the black wire of the PNP sensor and attach the multimeter's black lead to the ground.
- You expect if the PNP sensor does not sense the presence of a metal object, the PNP sensor's output voltage will be low, meaning the PNP sensor supplies almost zero volts to the input of the PLC module.
- And you expect if a metal object enters the PNP sensor detection range, the output voltage of the PNP sensor will be pulled up to almost nearly the same voltage of the power supply.
======================================================
⏰ TABLE OF CONTENTS ⏰
00:00 24-Volt DC Sensors
01:04 PNP Circuit
02:19 PNP Sensor Internal Diagram
03:00 PNP Sensor Connection
04:01 PNP Sensor Working Principle
04:55 PNP Sensor Wiring to PLC
06:36 PNP Sensor Testing
======================================================
🔥 Have you seen our recent popular videos? You can watch them here:
DCS Explained: • What is DCS? | Distributed Control Sy...
PLC Hardware: • PLC Hardware Components
PLC Explained: • PLC Explained | Programmable Logic Co...
HMI Explained: • What is HMI? | Human Machine Interface
SCADA Explained: • What is SCADA? | Supervisory Control ...
Photodiode Explained: • What is Photodiode? | Explained its W...
Capacitors Explained: • Capacitors Explained | Types and Appl...
RTD Sensors Explained: • Mastering RTD Sensors: Types, Compone...
RTU | Remote Terminal Unit: • What is RTU? | Remote Terminal Unit
Solenoid Valves Explained: • Solenoid Valve Explained | Types and ...
PLC Hardware Components: • PLC Hardware Components
Overload Relay Types & Trip Class: • Overload Relay Trip Class | Types of ...
IIoT | Industrial Internet of Things: • What is IIoT? | Industrial Internet o...
2-Wire, 3-Wire, and 4-Wire Transmitter: • 2-Wire, 3-Wire, and 4-Wire Transmitter
======================================================
💡 If you enjoyed this video and want to follow our upcoming videos, subscribe to this YouTube channel and relax your mind:
https://bit.ly/3CTjbUi
======================================================
#Automatedo #pnp #sensor








Информация по комментариям в разработке