The animation shows three weight matrices of a neural network as we train this network to find an approximate dominant eigenvector of an infinite dimensional linear operator.
Since the behavior of such networks is different every time I run the training, I will upload several visualizations of the training.
Let h=20. Let m=40. The neural network N is designed to approximate a dominant eigenvalue of a linear operator between infinite dimensional spaces. Before training the neural network, we generate random (but not Haar random) orthogonal matrices A,B. Our goal is to approximate a function f with mean 0 and where f(x)=c*(f(A*x)+f(B*x)) for all h dimensional vectors x with unit norm. The training data for the network shall consist of tuples of the form ((x_1,...,x_r),(y_1,...,y_r)) where x_j is a random unit vector of length h and where y_j=N(A*x_j)+N(B*x_j) for all j. Here, we select r=20.
The objective of the neural network N is to maximize the coefficient of determination (the linear correlation coefficient squared) between
(N(x_1),...,N(x_r)) and (y_1,...,y_r) for all training data points. The training data depends on the network N, so we update the training data after each iteration. The function f(x) can therefore be defined by f(x)=N(x)-E(N(X)).
Our technique for obtaining the function f combines gradient ascent with a version of the power iteration technique that can be used to find the dominant eigenvector of a matrix (the power iteration technique is the power behind algorithms like PageRank and the computation of LSRDRs).
The network (except for a very simple last layer) is of the form
Chain(Dense(h,m,atan),SkipConnection(Dense(m,m,atan),+),SkipConnection(Dense(m,m,atan),+),SkipConnection(Dense(m,m,atan),+),Dense(m,3,atan)). The weights in the layers with the skip connections were initialized at nearly zero.
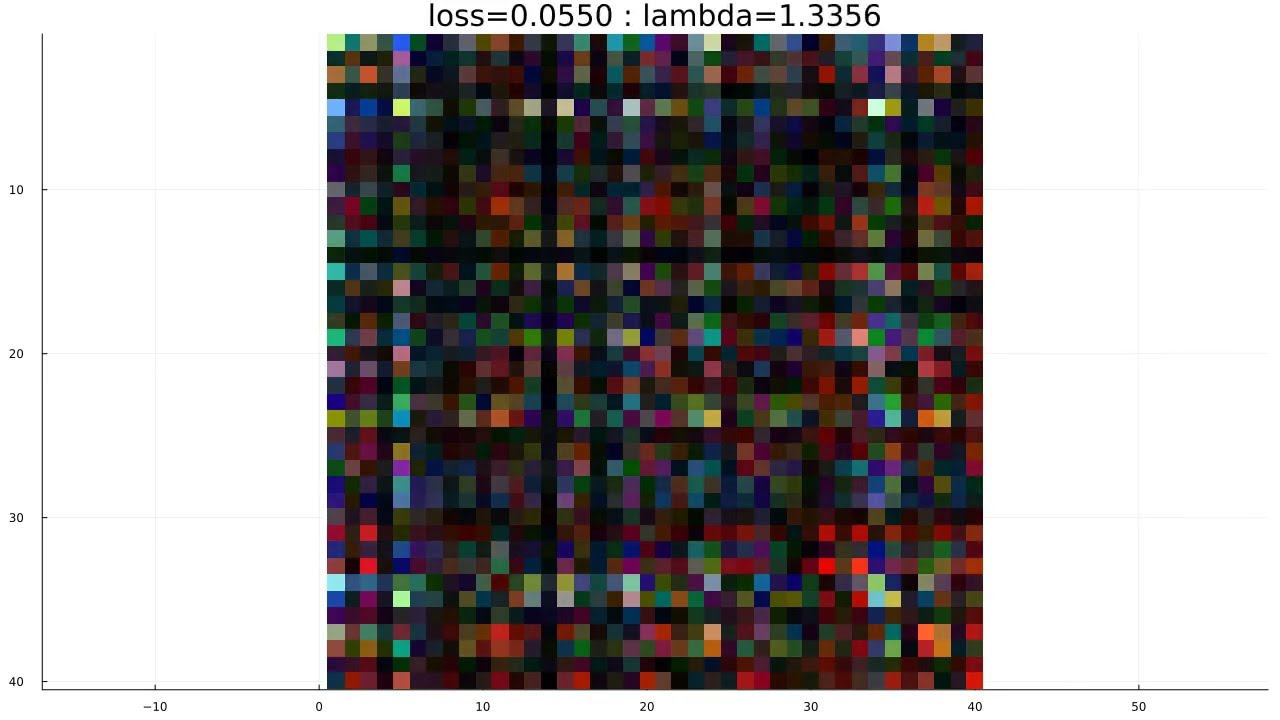
The animation shows the three m by m weight matrices of the layers with the skip connections between them. The three weight matrices are colored red,green, and blue. We observe that these weight matrices can be approximated by low rank matrices. Furthermore, since these weight matrices have little color to them, we observe that these three weight matrices are approximately equal to each other with the red weight matrix being nearly identical to the green weight matrix.
The value 'lambda' refers to the absolute value of the eigenvalue that was found.
Observe that since the training data for the network N changes over time, before running the experiment we have no reason to expect that the training of the neural network N would stabilize over time. In our case, the network oscillates between two solutions, but this is not always the case.
It is not to hard to reduce the problem of finding homogeneous polynomial solutions to the equation f(x)=c*(f(A*x)+f(B*x) to the problem of finding eigenvectors of linear operators between tensor products. In particular, the equation f(x)=c*(f(A*x)+f(B*x) has some linear solutions that the neural network can easily learn. On the other hand, the neural network N cannot easily learn higher degree polynomials, so it simply learns the linear solutions.
The notion of a neural network is not my own. I am simply making neural network animations to investigate some of the safety related properties of neural networks.
Unless otherwise stated, all algorithms featured on this channel are my own. You can go to https://github.com/sponsors/jvanname to support my research on machine learning algorithms. I am also available to consult on the use of safe and interpretable AI for your business. I am designing machine learning algorithms for AI safety such as LSRDRs. In particular, my algorithms are designed to be more predictable and understandable to humans than other machine learning algorithms, and my algorithms can be used to interpret more complex AI systems such as neural networks. With more understandable AI, we can ensure that AI systems will be used responsibly and that we will avoid catastrophic AI scenarios. There is currently nobody else who is working on LSRDRs, so your support will ensure a unique approach to AI safety.

Информация по комментариям в разработке