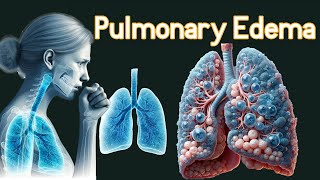
Pulmonary edema is fluid accumulation within the lungs.
Heavy wet lungs, full of fluid causes difficulty breathing, which is subjective experience of breathing discomfort.
May include other symptoms also.
coughing up blood (classically seen as pink, frothy and foamy sputum),
Excessive sweating, anxiety, and pale skin.
If, Shortness of breath manifest as orthopnea, Which means inability to lie down, flat due to breathlessness. and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, which means (episodes of severe sudden breathlessness at night).
It is sign of cardiac cause. Specifically left ventricular failure.
Other signs include end-inspiratory crackles (sounds heard at the end of a deep breath).
Pulmonary edema leads to impaired respiration and eventually respiratory failure.
3 main mechanisms exist, that can cause Pulmonary Edema.
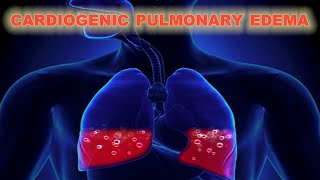
1. Increased hydrostatic Pressure. – Classic example is Left sided heart failure. Blood will back to lung and increased pressure in lungs causes blood leakage into capillaries. And we get pulmonary edema. Such edema is called cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
2. Decreased oncotic Pressure. For example if person has a liver disease, cirrhosis, the damaged liver can not produce enough albumins. It causes loosing oncotic pressure in blood vessels. And we get edema everywhere, including lungs.
3. Anything which can damage capillaries, can cause pulmonary edema. Because fluid can leak trough damaged capillaries.
Examples include: shock, radiation, infections in to the lungs. Heroine abuse.
Important and interesting type of pulmonary edema is High-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE). It is life-threatening form of non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema, that occurs in otherwise healthy people at altitudes typically above 2,500 meters.
Diagnosis
There is no single test for confirming pulmonary edema.
But chest X-ray will show fluid in the alveolar walls.
On X-ray you may see Kerley lines.
They are thin linear pulmonary opacities caused by fluid or cellular infiltration into the interstitium of the lungs.
Lung ultrasound also useful and CT scan is used to diagnose pulmonary edema.
Prevention:
Dexamethasone or, Sildenafil is in widespread use for the prevention of high altitude pulmonary edema.
Treatment:
Highly dependent on underlying cause.
But Hypoxia (abnormally low oxygen levels), may require supplementary oxygen.
if this is insufficient then again mechanical ventilation may be required to prevent complications.
Treatment of the underlying cause is the next priority. If it is caused by infection, it may requires antibiotics.
If cardiogenic, then Positioning upright may relieve symptoms. and A loop diuretic such as furosemide is administered.
By Mikael Häggström - Own work, CC0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...
By Patrick J. Lynch, medical illustrator - Patrick J. Lynch, medical illustrator, CC BY 2.5, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...
By Artwork by Holly Fischer - http://open.umich.edu/education/med/r... - Respiratory Tract Slide 20, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...
By Patrick J. Lynch, medical illustrator - Patrick J. Lynch, medical illustrator, CC BY 2.5, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...







Информация по комментариям в разработке