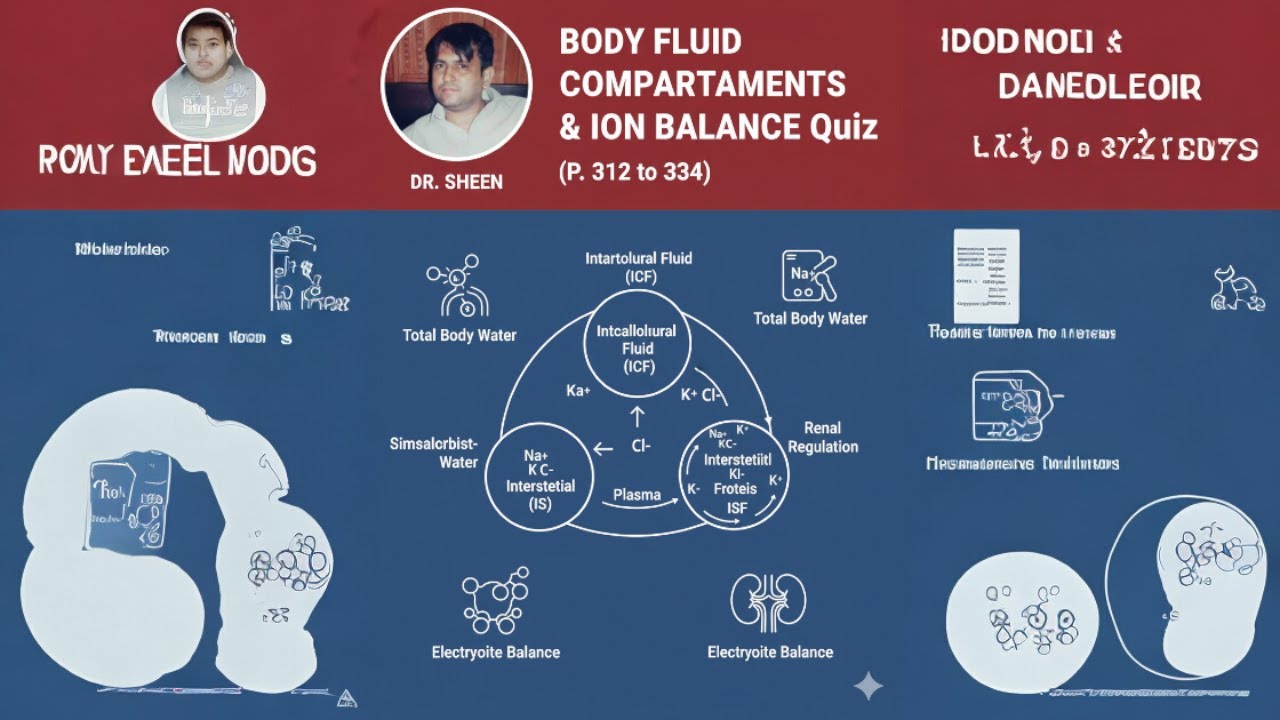
The body contains several major fluid compartments that together maintain internal balance. These compartments differ in size, contents, and how they exchange substances. Understanding them is essential for interpreting clinical conditions such as dehydration, edema, electrolyte imbalance, and blood loss.
1. Plasma and Interstitial Fluid
Plasma and interstitial fluid make up the extracellular fluid (ECF).
They have almost identical ionic composition because capillary membranes are highly permeable to most ions. The key difference is:
Plasma has more proteins, mainly albumin.
Capillaries restrict protein movement, so proteins remain mostly in plasma.
Donnan Effect
Plasma proteins carry negative charges, which affects the distribution of ions:
They attract cations (like sodium and potassium), so cation levels in plasma are slightly higher than in interstitial fluid.
They repel anions (like chloride), giving interstitial fluid slightly higher anion levels.
These differences are small, so clinically the ionic composition of plasma and interstitial fluid is considered nearly the same.
2. Composition of Extracellular Fluid
ECF contains:
High: Sodium, chloride, bicarbonate
Low: Potassium, magnesium, phosphate, organic ions
The kidneys regulate these ions to keep the environment stable for cells.
3. Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
The fluid inside cells differs significantly from ECF because the cell membrane:
Is highly permeable to water
Is not permeable to many ions
ICF composition:
High: Potassium, phosphate, magnesium, sulfate, proteins
Low: Sodium, chloride, calcium
Cells contain about four times more protein than plasma.
4. Measuring Fluid Compartments — Indicator Dilution Principle
The volume of a body fluid compartment can be measured by injecting a substance (indicator) that:
Mixes evenly throughout the compartment
Stays only in that compartment
Is not metabolized or excreted
After mixing, a sample is taken, and the final concentration is used to calculate the volume.
Basic formula:
Volume = (Amount injected) / (Final concentration)
Example: If 10 mg dye is injected and final concentration is 0.01 mg/mL → volume = 1000 mL
5. Measuring Specific Fluid Volumes
Different substances measure different compartments:
Total Body Water: tritium-labeled water, deuterium-labeled water, antipyrine
Extracellular Fluid: radioactive sodium, chloride, iothalamate, thiosulfate, inulin
Plasma Volume: 125I-albumin or Evans blue dye (binds plasma proteins)
6. Calculated Volumes
Some compartments cannot be measured directly and must be computed:
Intracellular Fluid = Total Body Water – Extracellular Fluid
Interstitial Fluid = Extracellular Fluid – Plasma
Blood Volume = Plasma Volume ÷ (1 – Hematocrit)
For example:
Plasma = 3 L, Hematocrit = 0.40 → Blood volume = 5 L
7. Blood Volume Measurement
Blood can also be measured by labeling a patient’s red blood cells with radioactive chromium and tracking dilution after reinjection.

Информация по комментариям в разработке