The Boston Massacre, known in Great Britain as the Incident on King Street, was a confrontation, on March 5, 1770, during the American Revolution in Boston in what was then the colonial-era Province of Massachusetts Bay.
In the confrontation, nine British soldiers shot several in a crowd estimated between 300 and 400, who were harassing them verbally and throwing various projectiles. The event was subsequently described as "a massacre" by Samuel Adams, Paul Revere, and other leading Patriots who later became central proponents of independence during the American Revolution and Revolutionary War. British troops had been stationed in the Province of Massachusetts Bay since 1768 in order to support Crown-appointed officials and to enforce unpopular legislation implemented by the British Parliament.
Amid tense relations between the civilians and the soldiers, a mob formed around a British sentry and verbally abused him. He was eventually supported by seven additional soldiers, led by Captain Thomas Preston, who were hit by clubs, stones, and snowballs. Eventually, one soldier fired, prompting the others to fire without an order by Preston. The gunfire instantly killed three people and wounded eight others, two of whom later died of their wounds.
The crowd eventually dispersed after acting governor Thomas Hutchinson promised an inquiry, but they reformed the next day, prompting the withdrawal of the troops to Castle Island. Eight soldiers, one officer, and four civilians were arrested and charged with murder, and they were defended in court by attorney, and future U.S. president, John Adams. Six of the soldiers were acquitted; the other two were convicted of manslaughter and given reduced sentences of branding on their hands.
Depictions, reports, and propaganda about the event, notably the colored engraving produced by Paul Revere, heightened tensions throughout the Thirteen Colonies.
On the evening of March 5, Private Hugh White stood on guard duty outside the Boston Custom House on King Street (today known as State Street). A wigmaker's apprentice, approximately 13 years old, named Edward Garrick called out to Captain-Lieutenant John Goldfinch, accusing him of refusing to pay a bill due to Garrick's master.
Goldfinch had settled the account the previous day, and ignored the insult. Private White called out to Garrick that he should be more respectful of the officer, and the two exchanged insults. Garrick then started poking Goldfinch in the chest with his finger; White left his post, challenged the boy, and struck him on the side of the head with his musket. Garrick cried out in pain, and his companion Bartholomew Broaders began to argue with White, which attracted a larger crowd. Henry Knox was a 19-year old bookseller who later served as a general in the revolution; he came upon the scene and warned White that, "if he fired, he must die for it."
As the evening progressed, the crowd around Private White grew larger and more boisterous. Church bells were rung, which usually signified a fire, bringing more people out. More than 50 Bostonians pressed around White, led by a mixed-race former slave named Crispus Attucks, throwing objects at the sentry and challenging him to fire his weapon. White had taken up a somewhat safer position on the steps of the Custom House, and he sought assistance. Runners alerted Captain Thomas Preston, the officer of the watch at the nearby barracks. According to his report, Preston dispatched a non-commissioned officer and six privates from the grenadier company of the 29th Regiment of Foot to relieve White with fixed bayonets. The soldiers were Corporal William Wemms and Privates Hugh Montgomery, John Carroll, William McCauley, William Warren, and Matthew Kilroy, accompanied by Preston. They pushed their way through the crowd. Henry Knox took Preston by the coat and told him, "For God's sake, take care of your men. If they fire, you must die." Captain Preston responded "I am aware of it." When they reached Private White on the custom house stairs, the soldiers loaded their muskets and arrayed themselves in a semicircular formation.
The crowd continued to press around the soldiers, taunting them by yelling "Fire!", by spitting at them, and by throwing snowballs and other small objects. Innkeeper Richard Palmes was carrying a cudgel, and he came up to Preston and asked if the soldiers' weapons were loaded. Preston assured him that they were, but that they would not fire unless he ordered it; he later stated in his deposition that he was unlikely to do so, since he was standing in front of them. A thrown object then struck Private Montgomery, knocking him down and causing him to drop his musket.
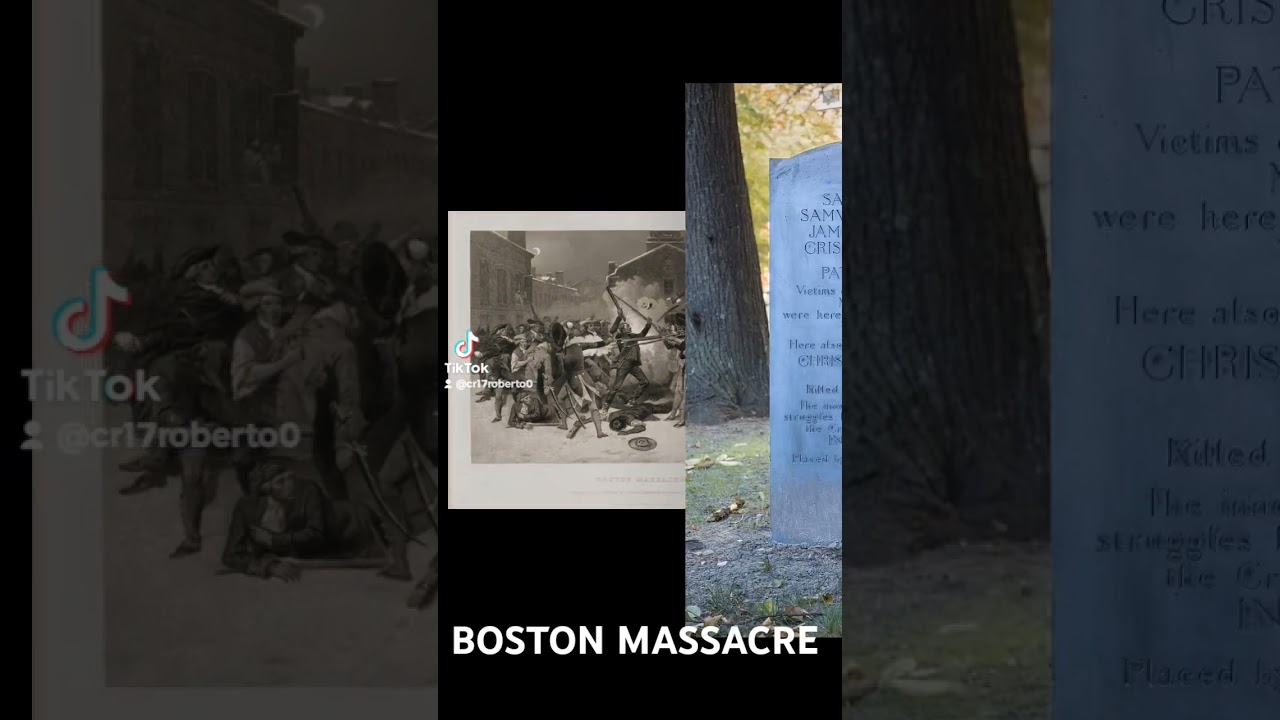
Информация по комментариям в разработке