Dr Himanshu Tyagi, Senior consultant Spine & Orthopaedic surgeon.
Phone : 9654095717
MCh Orthopaedics (U.K), FNB Spine surgery, DNB Orthopaedics.
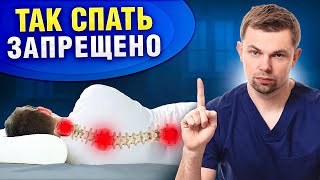
If a course of nonsurgical treatments (generally four to six weeks) is not effective for relieving pain from a herniated disc, lumbar decompression surgery may be considered as an option. Often a microdiscectomy (or microdecompression) - a type of lumbar decompression surgery - is used to treat nerve compression from a herniated disc
The microdiscectomy procedure is usually highly successful for relieving the leg pain (sciatica) caused by a herniated disc. Although the nerve root takes several weeks or months to fully heal, patients often feel immediate relief of their leg pain and usually have a minimal amount of discomfort following the surgery.
In general, if about six weeks of conservative treatment fails to relieve the arm pain or if the patient and the spine specialist determine that surgical removal of the disc is the best course of treatment, patients may consider anterior cervical decompression (discectomy). During this surgical procedure, the disc material is removed through the front of the neck and then the disc space is usually fused to keep the disc space open. Another surgical option to treat a herniated disc is a posterior cervical laminectomy, where the disc material is removed through the back of the neck.
During a minimally-invasive microdiscectomy procedure, the herniated portion of the disc under the nerve root is removed. By giving the nerve root more space, pressure is relieved and the nerve root can begin to heal.
The primary goal of treating a lumbar herniated disc is to reduce pain and other symptoms, not necessarily to correct the spine’s anatomy.
Most of the time, symptoms alleviate quickly on their own or using nonsurgical treatments. If such treatments are ineffective after 6 weeks, more robust, long-term methods may be considered. In some cases, surgery is necessary.
The first approach to treating lumbar herniated disc pain is the use of nonsurgical treatments, many of which can be administered at home and as appropriate. These treatments may include ice application, pain medications, muscle relaxants, heat therapy.
If these methods are unsuccessful after a few weeks, longer-term treatment options are typically recommended. These non-surgical treatments also tend to focus on pain relief, and can include epidural steroid injections, which administer a pain relief steroid directly to the outer portion of the spine; physical therapy and exercise, which work to strengthen the spine and its supporting muscles; spinal manipulation, as administered by a chiropractor, physiatrist, or specialist to adjust spinal structures to more comfortable positions; cognitive behavioral therapy, which helps many patients cope with the emotional effects of chronic pain; massage therapy, to ease muscle tension and spasms in the lumbar spine; and acupuncture, a practice based in ancient Chinese medicine that is said to restore balance to the body’s natural flow of energy.
Surgery for a lumbar herniated disc is only recommended if pain and other symptoms do not respond to nonsurgical treatments, or if low back or leg pain is so severe that it interferes with basic functions like sleeping, standing, or walking. Spinal surgery is not recommended for patients who are able to manage pain using other treatments.
The most common surgery used to treat a lumbar herniated disc is a microdiscectomy, in which a small incision of between one and one-and-a-half inches is made along the spine; the muscles surrounding the spine are pushed to the side and protective membranes are removed; the herniated disc portion of the disc is removed, reducing inflammation and irritation in the area and from the nearby nerve roots.
A microdiscectomy is a relatively minimally invasive procedure, and patients usually recover within 1 to 3 weeks. Residual leg pain or weakness may take a few weeks or months to heal, but most patients report immediate relief after the surgery is performed.
The kinds of treatment necessary to treat a lumbar herniated disc vary from person to person, and many people find that a combination of treatments is most effective for treating their pain.
#spine #backpain #spinehealth #spinesurgeon #slipdisc #drhimanshutyagi #bestspinesurgeon #scoliosis #scoliosistreatment #scoliosissurgery #kneepain #kneereplacement #kneesurgeon #kneearthritis #knee #kneepainhomeremedies #neckpain #neckpaintreatment #neck #cervicaldischerniation #cervicalpain #cervicalspondylosis #cervicalspine #cervical_spondylosis #lumbar #lumbarfusion #lumbarpain #lumbarspondylosis #lumbarspine #surgery #surgeryresults #surgery







Информация по комментариям в разработке