Welcome, medical students and USMLE examinees!, to a captivating exploration of immune checkpoint inhibitors—the cutting-edge tools in our arsenal against cancer.
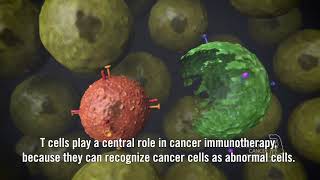
In this educational video, we delve into the intricate mechanisms of T cells as they wage war against cancer cells, driving them towards elimination while sparing healthy tissues. We also uncover the protective mechanisms of normal cells, which regulate T cell activity to maintain immune balance.
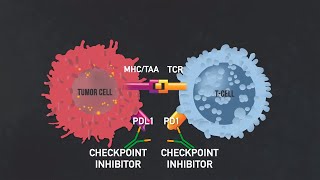
As aspiring healthcare professionals, you'll discover the strategic tactics employed by cancer cells to evade immune surveillance and how immune checkpoint inhibitors disrupt these evasion strategies, unleashing the full potential of T cell-mediated anti-cancer responses.
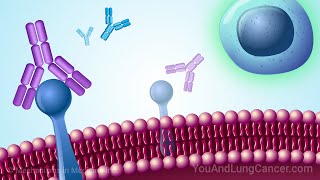
Join us in understanding the pivotal role of immune checkpoint proteins, the molecular orchestrators that fine-tune T cell activation, including PD-1 and PD-L1. Additionally, we explore the critical role of CTLA-4, a cell-surface receptor that dampens T cell activation by binding to B7-1/B7-2.
You'll delve into the remarkable advancements in immunotherapy with PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors like Cemiplimab, Nivolumab, Pembrolizumab, Atezolizumab, Durvalumab, and Avelumab, as well as CTLA-4 inhibitors like Ipilimumab.
Learn about
▹PD-1 inihibitors: Cemiplimab (Libtayo®), Nivolumab (Opdivo®), Pembrolizumab (Keytruda®)
▹PD-L1 inhibitors: atezolizumab (Tecentriq®), durvalumab (Imfinzi®), avelumab (Bavencio®).
▹CTRA-4 inhibitors: ipilimumab (Yervoy®)
#pharmacology #immunotherapy #cancertreatment
【Notes】
▹This video was created based on data as of March 2024, with the purpose of supporting medical students in their exam preparations.
▹Please note that thanks to the tireless efforts of researchers worldwide, this data is updated daily. ▹Unauthorized reproduction is prohibited.
【Contents】
00:00 immune checkpoint inhibitors, Basics
01:16 PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, Mechanism
02:24 CTLA-4 inhibitors, Mechanism
03:50 Side Effects, Mechanism
【Reference and figure】 I express my gratitude and respect for your wonderful achievements.
1. Zhang Y, Zheng J. Functions of Immune Checkpoint Molecules Beyond Immune Evasion. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1248:201-226. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-3266-5_9. PMID: 32185712.
2. NIH National cancer institute, “immune checkpoint inhibitor”
https://www.cancer.gov/publications/d...
3. Han Y, Liu D, Li L. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: current researches in cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Mar 1;10(3):727-742. PMID: 32266087; PMCID: PMC7136921.
4. Krummel MF, Allison JP. CD28 and CTLA-4 have opposing effects on the response of T cells to stimulation. J Exp Med. 1995;182:459–65.
5. Chen L. Co-inhibitory molecules of the B7-CD28 family in the control of T-cell immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:336–47.
6. Qin, S., Xu, L., Yi, M. et al. Novel immune checkpoint targets: moving beyond PD-1 and CTLA-4. Mol Cancer 18, 155 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-10...
7. Mansh M. Ipilimumab and cancer immunotherapy: a new hope for advanced stage melanoma. Yale J Biol Med. 2011 Dec;84(4):381-9. PMID: 22180676; PMCID: PMC3238313.
8. NIH National Cancer Institute, Definition of CTLA-4, https://www.cancer.gov/publications/d...
9. Choi J, Lee SY. Clinical Characteristics and Treatment of Immune-Related Adverse Events of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Immune Netw. 2020 Feb 17;20(1):e9. doi: 10.4110/in.2020.20.e9. PMID: 32158597; PMCID: PMC7049586.







Информация по комментариям в разработке