In this video we cover the basics on the chemical makeup of acids, bases, salts and the pH level.
Acids bases salts and ph level
Acids, bases and salts are inorganic substances that also belong to a group of compounds called electrolytes, which are substances that break up, or dissociate in solution, or water, to form charged particles or ions. The positive ions are called cations, and the negatively charged ions are called anions.
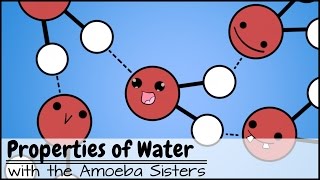
A water molecule is made up of an oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms that are covalently bonded, or share electrons with the oxygen atom. However, the electrons are not shared equally within the molecule, as they have a higher probability of being found closer to the nucleus of the oxygen atom, giving that end a slightly negative charge.
So, the hydrogen atoms end of the molecule will have a slightly positive charge. These charged ends weakly attach the positive end of one water molecule to the negative end of an adjacent water molecule. This is attraction or bonding is called a hydrogen bond.
Sometimes this attraction of a hydrogen atom of one water molecule to another molecule becomes so strong that it actually detaches from its original molecule and attaches to the other water molecule. So this yields a hydronium or h3o positive ion, and a hydroxide or oh negative ion.
Also, water molecules continually dissociate to form positive hydrogen ions and negative hydroxide ions; this is a reversible reaction as noted by the formula h20 double arrow, or reversible reaction, positive hydrogen ion and negative hydroxide ion. The actual amount of these positive h3o or hydrogen ions in water is actually very very small. To make things easier to understand we will consider the positive h3o ion and the positive hydrogen ion as one in the same. So, in pure water, the amount of positive hydrogen ions and negative oh ions is the same.
Now for acids. An acid is any substance that when added to an aqueous solution, or water, will release a hydrogen ion or increase the concentration of hydrogen ions. So, how strong an acid is depends on the amount of hydrogen ions produced.
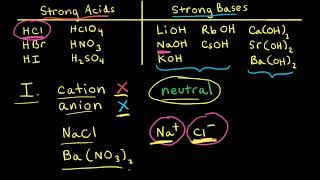
For instance hydrochloric acid or HCl, which is a hydrogen atom bonded to a chlorine atom, when added to solution or water will dissociate or break down into negative chlorine ions and positive hydrogen ions. Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid, as it completely dissociates in water.
Now for bases. Bases are essentially the opposites of acids, in that they shift the hydrogen ion hydroxide ion balance in favor of the negative hydroxide ion. This can be done by increasing the number of hydroxide ions, or decreasing the number of hydrogen ions. For instance, sodium hydroxide or NaOh, will break down, or dissociate into positive Na ions and negative oh ions.
So, the balance has shifted in favor of the negative hydroxide ions, meaning sodium hydroxide is a base. Bases can also be strong or weak depending on how well they break apart, sodium hydroxide is a strong base.
This brings us next to the ph scale, which is basically an abbreviation for the phrase “the power of hydrogen”. So, the ph scale measures the concentration of hydrogen ions of a solution, or it measures how acidic or basic a substance is. As the amount of positive hydrogen ions increases, the ph goes down, and the solution becomes more acidic. As the amount of positive hydrogen ions decreases, the ph goes up, and the solution becomes more basic.
On a ph scale, a ph of 7 means the solution is neutral, or the number of positive hydrogen ions equals the number of negative hydroxide or oh ions. A ph of less than 7 means the solution is more acidic or more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions, and a ph of greater than 7 means the solution is more basic, or more hydroxide ions than hydrogen ions.
On the scale, hydrochloric acid, which we mentioned earlier, and is a produced in the stomach, is at the most acidic end having a ph of zero, vinegar has a ph of 3, coffee has a ph of 5, and pure water has ph of 7, making it neutral. On the opposite end, sodium hydroxide, which we mentioned earlier, is at the most basic or alkaline end having a ph of 14, ammonia has a ph of about 11, and baking soda has a ph of between 8 and 9.
Now we can look at salts. A salt is a chemical compound formed from the reaction of an acid with a base. So, hydrochloric acid, hcl can interact with sodium hydroxide naoh, a base, and form sodium chloride nacl and water h2o.
Timestamps
0:00 What are acids, bases and salts (overview)?
0:24 The structure of a water molecule as an example
2:10 What are acids?
2:49 What are bases?
3:32 The pH scale
5:02 What are salts?








Информация по комментариям в разработке