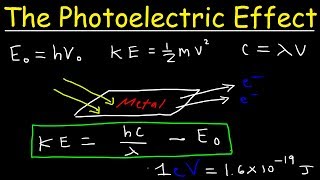
Calculate the work function in eV and calculate the stopping potential in the photoelectric effect.
Скачать Calculate the work function in eV and calculate the stopping potential in the photoelectric effect. бесплатно в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете скачать бесплатно Calculate the work function in eV and calculate the stopping potential in the photoelectric effect. или посмотреть видео с ютуба в максимальном доступном качестве.
Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Cкачать музыку Calculate the work function in eV and calculate the stopping potential in the photoelectric effect. бесплатно в формате MP3:
Если иконки загрузки не отобразились, ПОЖАЛУЙСТА,
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если у вас возникли трудности с загрузкой, пожалуйста, свяжитесь с нами по контактам, указанным
в нижней части страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса video2dn.com







![Почему простые числа образуют спирали? [3Blue1Brown]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/DxntHp7-wbg/mqdefault.jpg)

Информация по комментариям в разработке