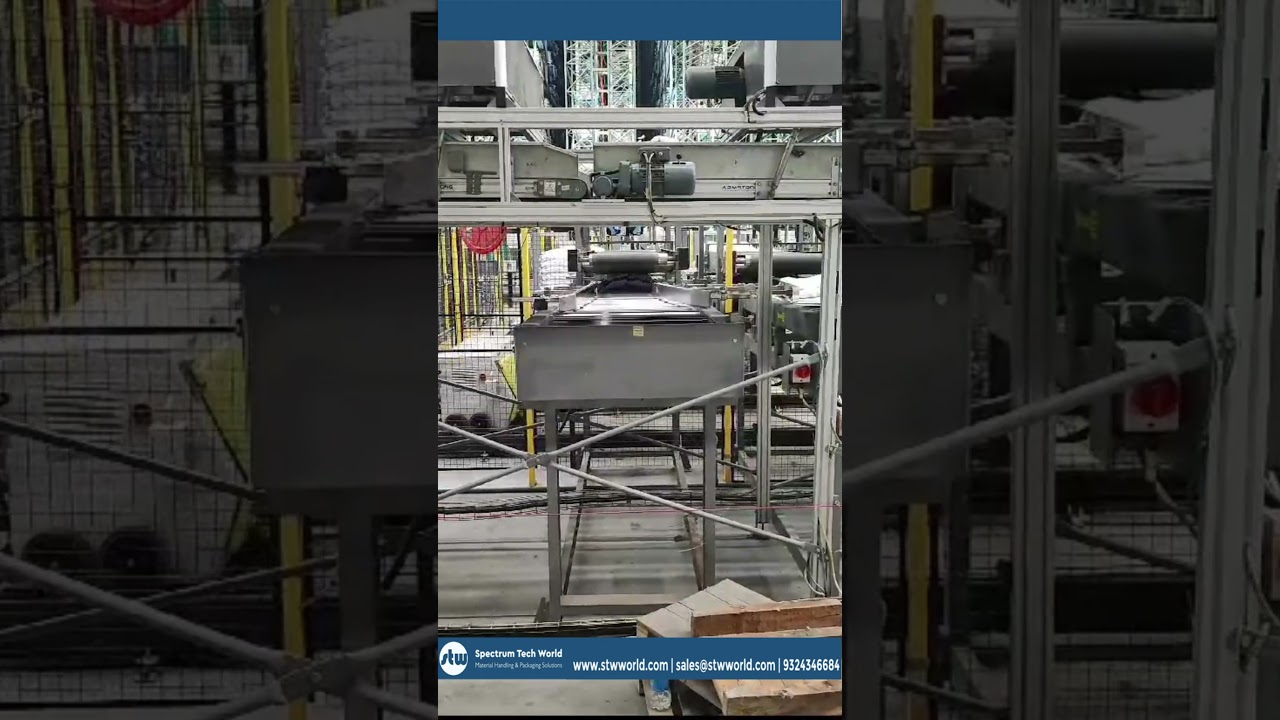
A belt conveyor is a continuous transport system consisting of two or more pulleys (or drums), with a closed loop of material—typically made of rubber, fabric, or metal—rotating around them. The pulleys are powered to drive the conveyor belt, which moves in a horizontal or inclined direction to transport materials from one location to another.
Key Components of a Belt Conveyor:
1. Belt: The actual moving element that transports materials. It can be made from various materials depending on the application.
2. Pulleys: The wheels that the belt wraps around. The drive pulley is powered to move the belt, and the take-up pulley helps maintain tension and align the belt.
3. Structure: The frame that supports the belt and its components. It can be made of metal or other sturdy materials.
4. Motor: Provides the power to move the belt, often through a system of gears or pulleys.
5. Idlers: Rollers that support the belt along its path, ensuring smooth movement and providing stability.
6. Control System: Manages the operation, speed, and flow of materials on the conveyor.
Uses of Belt Conveyors
1. Material Handling: Belt conveyors are widely used in warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing plants for transporting materials such as packages, pallets, and loose items.
2. Mining and Quarrying: They are essential for the bulk transport of materials like coal, ore, gravel, and other minerals in mining operations.
3. Food Industry: Used for moving bulk food items, packaging, and processing operations. They can be designed to meet hygiene standards.
4. Agriculture: Used to transport agricultural products like grains, vegetables, and other bulk items from one point to another.
5. Recycling: They play a critical role in sorting and transporting recyclables in waste management facilities.
6. Construction: Used to transport heavy materials like sand, gravel, or precast elements across construction sites.
Applications of Belt Conveyors
1. Manufacturing Lines: In assembly lines to move components between workstations, ensuring efficient production processes.
2. Shipping and Packaging: Loading and unloading packages onto trucks or containers, improving efficiency in logistics.
3. Mining Operations: For transporting mined minerals from the extraction site to processing facilities or loading areas.
4. Airport Baggage Handling: Moving luggage from check-in counters to the aircraft and vice versa.
5. Power Plants: Transporting coal or other fuels to the boiler for energy generation.
6. Automotive Industry: Moving parts and assembled vehicles through various stages of production.
7. Food Processing: Transporting raw materials, intermediate products, and finished goods in food production facilities.
Advantages of Belt Conveyors
• Efficiency: Continuous operation and high capacity for transporting materials.
• Versatility: Can be used for various materials and across various industries.
• Low Energy Consumption: Modern systems are designed to minimize energy usage.
• Customization: Can be customized in length, width, and material to suit specific needs.
• Easy Maintenance: Relatively simple design allows for easier maintenance and repairs.

Информация по комментариям в разработке