Upper and lower motor neuron diseases: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Progressive bulbar palsy (PBP), Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS), Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) - Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, Kugelberg-Welander disease, Spinobulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA) - Kennedy’s disease, Post-polio syndrome (PPS). Symptoms, diagnosis, progression, expected lifespan.
This video is available for instant download licensing here: https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/g...
©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved.
Voice by : Marty Henne
Support us on Patreon and get early access to videos and free image downloads: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia
All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Motor neuron disease is a group of rare neurological conditions in which motor neurons - the nerve cells that control skeletal muscle movement – are progressively degenerated. Loss of motor neurons results in muscle weakness that gradually worsens over time, impairing the body’s ability to move, eat, speak, or even breathe.
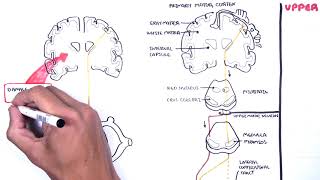
Usually, motor instructions from the brain are transmitted to the muscles via 2 neurons: an upper motor neuron starts in the primary motor cortex of the cerebrum; and a lower motor neuron continues from the brainstem or spinal cord, forming the corticobulbar and corticospinal tracts, respectively. The corticobulbar tracts control muscles of the face, head, and neck and are responsible for facial expression, speech, swallowing, among others. The corticospinal tracts control muscles of the torso and limbs.
Lesions of upper and lower motor neurons affect the muscles in different ways. A loss of upper motor neuron function often leads to increased muscle tone, muscle stiffness, known as spasticity, and overresponsive reflexes. On the other hand, lower motor neuron lesions often result in reduced muscle tone, flaccid paralysis, and muscle wasting and twitching.
The many forms of motor neuron disease are classified according to whether the loss of neuron function is inherited or sporadic, and whether the condition affects upper or lower motor neurons.
The most common form is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, ALS, which affects both upper and lower motor neurons. Patients typically present with spastic paralysis and overactive reflexes in the lower limbs; and flaccid paralysis and reduced responses in the upper limbs, along with tongue twitching. In the later stage, symptoms may also include slurred speech, and difficulty swallowing and breathing. Most people with ALS die from respiratory failure, typically within a few years from diagnosis, although a small number of patients may survive for a much longer time. ALS usually strikes in midlife, but it can occur in people of any age. Most ALS cases are sporadic, only about 10% are inherited, with at least a dozen of genes involved.
Progressive bulbar palsy, PBP, affects the lower motor neurons that originate from the brainstem, also known as the bulbar region. Symptoms include difficulty chewing, swallowing, and speaking. PBP is sometimes considered a subtype of ALS, because most PBP patients eventually also develop widespread muscle weakness.
Primary lateral sclerosis, PLS, affects only upper motor neurons. PLS progresses much more slowly than ALS and is not usually fatal. However, because a number of ALS cases start out as PLS, a PLS diagnosis is considered definitive only after at least 4 years.
Spinal muscular atrophy, SMA, is a group of genetic disorders affecting lower motor neurons. There are many different forms of SMA, caused by mutations in different genes, with different modes of inheritance. The three main forms are due to defects in the same SMN1 gene (autosomal recessive), but differ in age of onset, severity.
Spinobulbar muscular atrophy, or Kennedy’s disease, is a form of SMA caused by mutations in the androgen receptor gene on the X chromosome. This disease typically strikes in adulthood and affects mostly men (X-linked inheritance). Early symptoms include tremor, lower limb weakness, and tongue twitching. Late symptoms include widespread muscle weakness and wasting. The disease however progresses very slowly, with most patients having a normal lifespan.
Post-polio syndrome, PPS, is a condition that affects polio survivors, sometimes decades after the initial illness. Symptoms include muscle and joint weakness and pain, twitches, muscle wasting, and intolerance to cold. Some patients may also have difficulty breathing and swallowing. PPS is usually not fatal.
There is no cure for motor neuron disease, but supportive treatments can relieve symptoms and may help maintain quality of life.







Информация по комментариям в разработке