This video shows Inguinal Hernia.
A hernia occurs when an organ or fatty tissue squeezes through a weak spot in a surrounding muscle or connective tissue called fascia. The most common types of hernia are inguinal (inner groin), incisional (resulting from an incision), femoral (outer groin), umbilical (belly button), and hiatal (upper stomach).
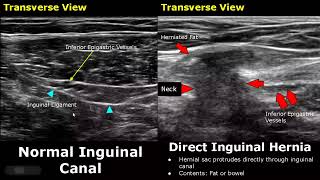
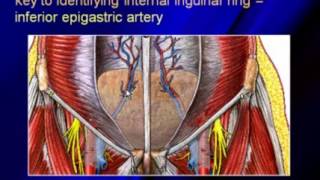
An inguinal hernia occurs when tissue, such as part of the intestine, protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles. The resulting bulge can be painful, especially when you cough, bend over or lift a heavy object.
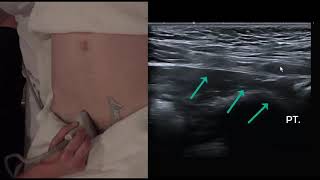
Ultrasound is a non-invasive, non-ionizing radiation modality that is highly successful at soft tissue imaging. Groin pain from an occult hernia can be a difficult clinical diagnosis made easier by good imaging by optimizing the image using depth, focus, and gain.
Ultrasound findings
1). Herniated gut loops along with some fluid collection at the Inguinal region.
2). Testis and epididymis pulled up with herniated contents.
3). Hydrocele on the respective involved side.
4). Normal testis on the unaffected side.
A bulge in the groin area is visible. Because standing and coughing can make a hernia more prominent, you'll likely be asked to stand and cough or strain. If the diagnosis isn't readily apparent, your doctor might order an imaging test, such as an abdominal ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI.
Examination of an adult for an inguinal hernia is best performed from the seated position, with the patient standing. The inguinal canal areas for the bulge are visualized. A provocative cough may be necessary to expose the hernia; the cough is repeated as the examiner invaginates the scrotum and feels for an impulse.
Not all inguinal hernias need to be repaired, but all hernia repairs require surgery. Small hernias that are not strangulated, not blocking the blood supply to the intestine, and are not causing bowel obstruction or significant pain do not necessarily require surgery or emergency surgical repair.
An inguinal hernia isn't necessarily dangerous. But it doesn't improve on its own and can lead to life-threatening complications. Your doctor is likely to recommend surgery to fix an inguinal hernia that's painful or enlarging.
Hernias can go misdiagnosed in women, and can instead be thought to be ovarian cysts, fibroids, endometriosis, or other abdominal issues, according to the SLS. Women's hernias can be small and internal. They might not be a bulge that can be felt in an exam or be visible outside the body.
Usually, the bulge is soft enough that you can gently push, or knead, it back into your abdomen (reducible), and it is often not there when you wake up in the morning. Most hernias are not painful. However, sometimes the area around your hernia may be tender and you may feel some sharp twinges or a pulling sensation.






Информация по комментариям в разработке