Discover the best way to handle exceptions in Spring Boot using `@ ControllerAdvice` and ensure a robust application!
---
This video is based on the question https://stackoverflow.com/q/64764393/ asked by the user 'H Athukorala' ( https://stackoverflow.com/u/9403408/ ) and on the answer https://stackoverflow.com/a/64764509/ provided by the user 'Nakul Goyal' ( https://stackoverflow.com/u/13127098/ ) at 'Stack Overflow' website. Thanks to these great users and Stackexchange community for their contributions.
Visit these links for original content and any more details, such as alternate solutions, latest updates/developments on topic, comments, revision history etc. For example, the original title of the Question was: What is the best way to handle exception in Spring Boot?
Also, Content (except music) licensed under CC BY-SA https://meta.stackexchange.com/help/l...
The original Question post is licensed under the 'CC BY-SA 4.0' ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/... ) license, and the original Answer post is licensed under the 'CC BY-SA 4.0' ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/... ) license.
If anything seems off to you, please feel free to write me at vlogize [AT] gmail [DOT] com.
---
The Best Practices for Exception Handling in Spring Boot
In the world of application development, handling exceptions gracefully is a crucial skill. When developing an application in Spring Boot, you might find yourself wondering about the best ways to manage exceptions. More specifically, you may ask: What is the best way to handle exceptions in Spring Boot? In this post, we will explore the effective practices for exception handling in Spring Boot, focusing on the use of @ ControllerAdvice and @ RestControllerAdvice annotations.
Understanding the Exception Handling Flow in Spring Boot
ExceptionHandler Class
Let's take a closer look at the example shared by our developer. They have created an ExceptionHandler class that uses the @ ControllerAdvice annotation to handle exceptions globally across the controllers.
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
@ ControllerAdvice: This annotation allows you to handle exceptions across all controllers in one global handling component. This means you don't need to repeat your error handling code in every controller.
Service Layer with Exception Throwing
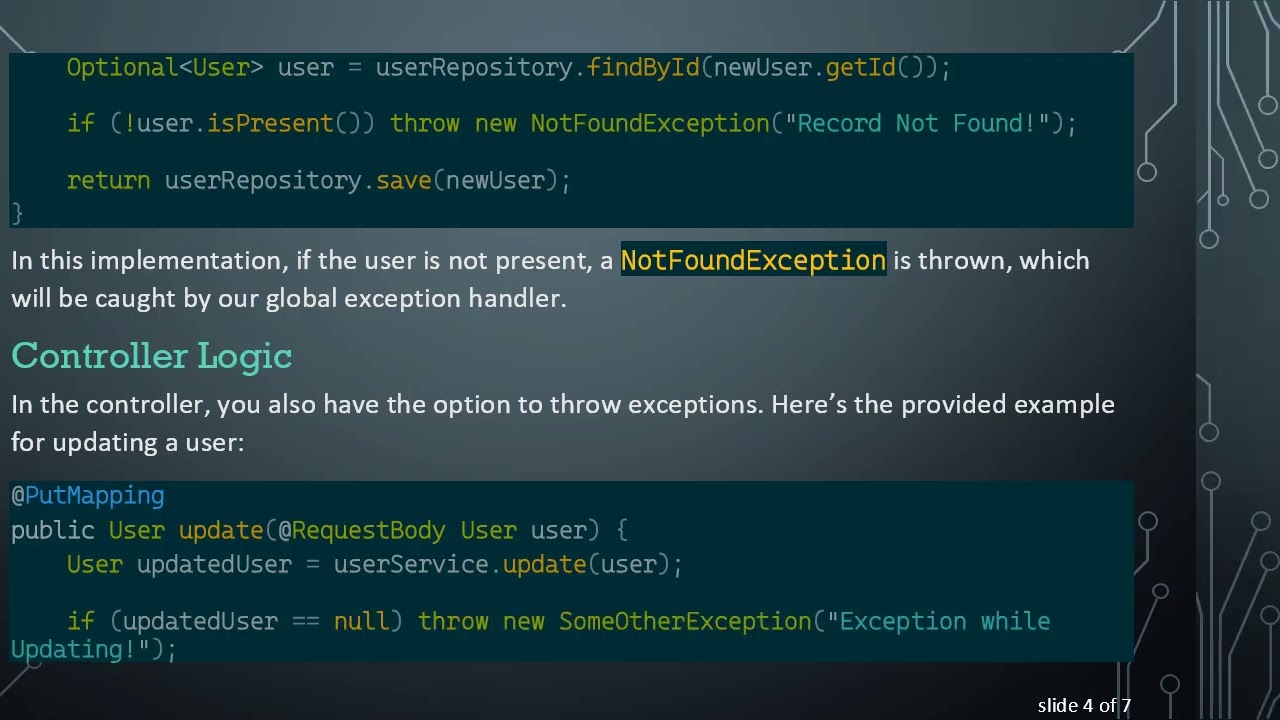
In your service layer, you may want to throw exceptions when certain conditions are not met. Here's how the developer implemented their service method:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
In this implementation, if the user is not present, a NotFoundException is thrown, which will be caught by our global exception handler.
Controller Logic
In the controller, you also have the option to throw exceptions. Here’s the provided example for updating a user:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
Best Practices for Exception Handling
1. Use @ ControllerAdvice or @ RestControllerAdvice
@ ControllerAdvice: Use this for applications where you want to handle exceptions for traditional MVC controllers that return views (HTML).
@ RestControllerAdvice: Prefer this for RESTful APIs that return JSON responses. This annotation implicitly adds @ ResponseBody to all methods, so you can handle exceptions and return JSON objects easily.
2. Manage Exceptions Across Layers
It's perfectly acceptable to throw exceptions from any layer of your application, whether it’s in your service or controller. The global @ ControllerAdvice will catch exceptions thrown in both layers, providing a centralized error handling mechanism.
3. Customize Your Exception Responses
Using a class like ErrorResponse is a good practice to encapsulate the error details you want to return to users. You can enhance this class to include additional information regarding the errors such as timestamps, error codes, or user-friendly messages.
4. Don't Throw Unchecked Exceptions for Business Logic
While throwing exceptions is a good technique for handling error states, it's important to only throw exceptions that are relevant to business logic. Avoid throwing unchecked exceptions unless it’s truly necessary, as this makes your application less predictable.
Conclusion
Handling exceptions in Spring Boot can seem daunting, but by using @ ControllerAdvice or @ RestControllerAdvice, you can centralize and streamline your error management procedures. Both of these approaches allow throwing exceptions at any service layer and automatically catching them, ensuring a consistent response across your application.
By following the outlined best practices, you will improve the robustness of your Spring Boot applications and deliver a better user experience during error states.
Final Thoughts
In summary, embracing structured exception handling in Spring Boot not only keeps your code clean and maintainable but also enhances your application's resilience. Feel free to implement these recommendations and watch

Информация по комментариям в разработке