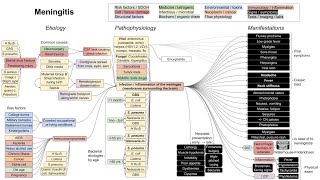
This is a mechanism of disease flowchart for cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, and other associated complications, covering the etiologies, pathophysiologies, and manifestations of these conditions.
ADDITIONAL TAGS:
Forty (40) years of age
Obstruction / mass effect
Signs / symptoms
Labs / tests / imaging results
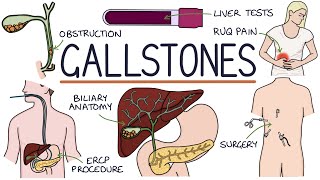
Cholelithiasis, Cholecystitis
Core concepts
Social determinants of
health / risk factors
Pharmacology / toxicity
Microbial pathogenesis
Biochem / organic chem
Flow gradients
Genetics / hereditary
Inflammation
Pathophysiology
Etiology
Manifestations
Passage of gallstones into the cystic duct
Cystic duct obstruction
Distension of gallbladder
Inflammation: release of cytokines / mediators that initiate a reaction
+/- bowel pathogens (E. coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Enterococcus) infiltrate the bile ducts
Local bacterial infection
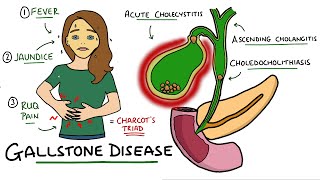
RUQ pain
-More severe, prolonged (6hrs) than biliary colic
-Fatty meal → gallbladder contracts to release bile into the duodenum to aid in digestion by emulsifying fats → postprandial pain
Irritates phrenic nerve
Pain radiates to right scapula
Inspiration → gallbladder pushed caudally
Positive Murphy sign: sudden pause during inspiration w deep palpation of RUQ
Guarding
Fever
Anorexia, malaise
Nausea, vomiting
Complications
-Ischemic necrosis → gangrenous cholecystitis
Ischemic necrosis → break in gallbladder wall → perforation → biliary peritonitis +/ hemorrhagic cholecystitis
-Cholelithiasis → chronic irritation → recurrent but self-limiting acute cholecystitis → chronic cholecystitis → gallbladder cancer, porcelain gallbladder, cholecystoenteric fistula → gallstone ileus
-Bacterial infiltration → gallbladder empyema (suppurative cholecystitis)
-Bacterial infiltration → pericholecystic, pyogenic liver, or subhepatic abscess
Formation of chole- sterol stones (95%)
Abnormal hepatic cholesterol metabolism
↑ cholesterol in bile + ↓ bile salts → hypersaturated bile
Cholesterol and calcium carbonate precipitate
Fat: obesity, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia
↑ estrogen
Female sex
Fertile (pregnant or multiparity)
↑ progesterone
Biliary stasis
Smooth muscle relaxation
↓ gallbladder contraction
Fair-skin: European, Hispanic, Native Amer.
Family history
Fibrates (inhibit cholesterol 7-α hydroxylase)
Estrogen therapy; OCPs
Malabsorption (Crohn, ileal resection, CF)
Formation of black pigment stones (10%)
Bilirubin polymers precipitate
↑ uptake, ↑ conjugation of bilirubin
↑ circulating unconjugated bilirubin
SCD; hereditary spherocytosis
↑ hemolysis
Alcoholic cirrhosis
Total parenteral nutrition
Formation of mixed / brown pigment stones (10%)
calcium carbonate, cholesterol, and calcium bilirubinate precipitate
↑ unconj. bili and ↑ fatty acids
Infection of the biliary tract (gut bacteria, Clonorchis sinensis, Opisthorchis species)
Bacteria and injured hepatocytes release β-glucuronidase
Hydrolysis and conjugation of bilirubin in bile
Reduced perfusion of gallbladder → acute acalculous cholecystitis
Critical illness (surgery, trauma, burns, multiorgan failure, infxn → septic shock, TPN, immunodeficiency)
Gas-forming bacteria (Clostridium spp., E.coli) → emphysematous cholecystitis → air within gallbladder wall/lumen
RUQ u/s: GB wall thick (3 mm), wall edema, GB distention (40 mm), pericholecystic and perihepatic (C sign) fluid







Информация по комментариям в разработке