The International Organization for Standardization is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.
ISO was founded in 1947, and (as of November 2022) it has published over 24,500 international standards covering almost all aspects of technology and manufacturing. The organization develops and publishes standardization in all technical and nontechnical fields other than electrical and electronic engineering. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland,[8] and works in 167 countries as of 2022.
ISO 15189 dictates minimum standards that Medical Laboratories must have in place, in order to be Accredited or Certified.
There are 12 Quality Essentials that ISO 15189 recommends for ensuring quality.
Below are the 12 essentials written by Robert Fenton from Qualio:
A laboratory's Quality Management System should cover all aspects of its processes and procedures. The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) and ISO 15189 sets out the following 12 essentials for quality
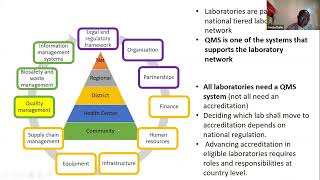
1. Organization
The laboratory needs to be organized around a formal quality management system that supports consistent procedures. The management team and quality unit play an integral role in a quality-driven culture, along with structures for monitoring ongoing quality.
2. Personnel
Capable, qualified staff members are the single most important asset to a laboratory. Training, motivation, and engagement are key parts of the quality management system. You also need to document all of your training processes within your quality management system.
3. Equipment
Every piece of equipment used in the laboratory must be maintained to operate safely. Also, laboratories need to monitor how equipment is installed, which suppliers provide the equipment, any calibration processes, and when the equipment needs to be replaced to maintain the highest possible quality.
4. Purchasing and Inventory
Properly managing the supply chain is critical to ensure that raw inputs and other supplies are consistently high-quality. Inventory activities should verify that materials and supplies are stored in a way that protects integrity. Make sure you purchase inventory from suppliers who also follow a quality management system.
5. Process Control
Process control encompasses QC processes for testing, including:
Collection
Handling
Method Verification
Process Validation
6. Information Management
The laboratory produces many forms of information, including QC test results, maintenance reports, and other data. Along with that, the lab processes patient information such as medical exams, results, and more. This data needs to be managed in a way that ensures all information is accurate, secure, confidential, and accessible to individuals with the right privileges, such as lab managers and leadership.
7. Documents and Records
Documents are a similar concept to information management, and there's a significant overlap between these categories. One of the most essential lab documents is standard operating procedures (SOPs) to create a standard for each process. Documents need to be available at the point of work, maintained, accurate, and secure.
8. Occurrence Management
An "occurrence" is any error or non-conformance. A QMS software can help you detect these issues and facilitate investigations to discover the root cause and prevent reoccurrence. A laboratory QMS can also assist you if you're going through an audit, as it's much easier to document these occurrences and what you did to fix them.
9. Assessment
Assessment involves comparing laboratory performance to internal standards for quality or external data sets, such as industry benchmarks. Assessments include the activities of lab or QC managers, internal auditors, or external inspectors.
10. Process Improvement
A quality management system should support the continuous improvement of laboratory processes. Components of the QMS which support improvement can include quality assurance, quality control, and CAPA (occurrence management).
11. Customer Service
Customer service is the ultimate goal of a laboratory. A laboratory's QMS should support operations that consistently provide a positive customer experience through the production of consistently high-quality products or other missions. The laboratory needs to understand the customers and their needs and use customer feedback for improvement.
12. Facilities and Safety
Laboratories need a comprehensive set of procedures and standards to ensure a safe, secure, and clean environment. This includes physically securing the lab, containment procedures for hazards, worker safety, and ergonomics.









Информация по комментариям в разработке