The urinary tract includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Within each kidney, urine flows from the outer cortex to the inner medulla. The renal pelvis is the funnel through which urine exits the kidney and enters the ureter.
As urine can become very concentrated as it passes through the kidneys. When the urine becomes too concentrated, calcium, uric acid salts and other chemicals dissolved in the urine can crystallize, forming a kidney stone (renal calculus).
Usually the calculus is the size of a small pebble. But ureters are very sensitive to being stretched, and when stones form and distend it, the stretching can be very painful. Often, people may not know they have kidney stones until they feel the painful symptoms resulting from a stone being stuck anywhere along the urinary tract. Fortunately, small stones typically pass out of the kidneys and through the ureters on their own without causing any problems.
However, stones can become more problematic when they block the flow of urine. A staghorn kidney stone may obstruct the entire kidney. Fortunately, these stones are the exception rather than the rule.
Kidney stone disease, also known as urolithiasis, is when a solid piece of material (kidney stone) occurs in the urinary tract. Kidney stones typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine stream. A small stone may pass without causing symptoms. If a stone grows to more than 5 millimeters (0.2 in) it can cause blockage of the ureter resulting in severe pain in the lower back or abdomen. A stone may also result in blood in the urine, vomiting, or painful urination. About half of people will have another stone within ten years.
Most stones form due to a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Risk factors include high urine calcium levels, obesity, certain foods, some medications, calcium supplements, hyperparathyroidism, gout and not drinking enough fluids. Stones form in the kidney when minerals in urine are at high concentration. The diagnosis is usually based on symptoms, urine testing, and medical imaging. Blood tests may also be useful. Stones are typically classified by their location: nephrolithiasis (in the kidney), ureterolithiasis (in the ureter), cystolithiasis (in the bladder), or by what they are made of (calcium oxalate, uric acid, struvite, cystine).
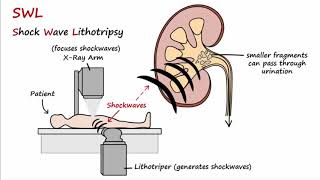
In those who have had stones, prevention is by drinking fluids such that more than two liters of urine are produced per day. If this is not effective enough, thiazide diuretic, citrate, or allopurinol may be taken. It is recommended that soft drinks containing phosphoric acid (typically colas) be avoided. When a stone causes no symptoms, no treatment is needed. Otherwise pain control is usually the first measure, using medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or opioids. Larger stones may be helped to pass with the medication tamsulosin or may require procedures such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy, ureteroscopy, or percutaneous nephrolithotomy.
Between 1% and 15% of people globally are affected by kidney stones at some point in their lives. In 2015, 22.1 million cases occurred, resulting in about 16,100 deaths. They have become more common in the Western world since the 1970s. Generally, more men are affected than women. Kidney stones have affected humans throughout history with descriptions of surgery to remove them dating from as early as 600 BC.
Signs and symptoms
The hallmark of a stone that obstructs the ureter or renal pelvis is excruciating, intermittent pain that radiates from the flank to the groin or to the inner thigh. This pain, known as renal colic, is often described as one of the strongest pain sensations known. Renal colic caused by kidney stones is commonly accompanied by urinary urgency, restlessness, hematuria, sweating, nausea, and vomiting. It typically comes in waves lasting 20 to 60 minutes caused by peristaltic contractions of the ureter as it attempts to expel the stone.
The embryological link between the urinary tract, the genital system, and the gastrointestinal tract is the basis of the radiation of pain to the gonads, as well as the nausea and vomiting that are also common in urolithiasis. Postrenal azotemia and hydronephrosis can be observed following the obstruction of urine flow through one or both ureters.
Pain in the lower-left quadrant can sometimes be confused with diverticulitis because the sigmoid colon overlaps the ureter, and the exact location of the pain may be difficult to isolate due to the close proximity of these two structures.
Risk factors
Dehydration from low fluid intake is a major factor in stone formation. Obesity is a leading risk factor as well.
High dietary intake of animal protein, sodium, sugars including honey, refined sugars, fructose and high fructose corn syrup, oxalate, grapefruit juice, and apple juice may increase the risk of kidney stone formation.









Информация по комментариям в разработке