Subscribe for a fun approach to learning lab techniques: / @adwoabiotech
PBMC ISOLATION
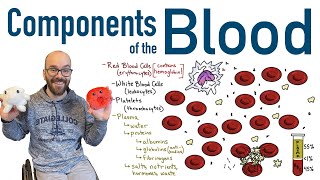
Whole blood contains a range of cells such as lymphocytes (B and T cells), monocytes (precursors to macrophages), granulocytes, red blood cells (aka erythrocytes) and platelets (aka thrombocytes).
A Peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) is any blood cell that has a round nucleus such as lymphocytes, monocytes or macrophages. To isolate the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs; monocytes, lymphocytes and a small percentage of other immune cells such as dendritic cells ), fresh blood is collected in EDTA (purple-capped) blood tubes or lithium/heparin (green-capped) tubes, to prevent clotting of the blood. The blood is then diluted with an equal volume of phosphate buffered saline before layering on top of Ficoll reagent. Ficoll is a highly branched sucrose polymer (polysaccharide) that does not penetrate biological membranes. Alternatively, glass tubes pre-filled with ficoll - called Cell Preparation Tubes (CPT) - may be used to extract PBMCs from whole blood.
Centrifugation is performed to separate the cells according to density. Ficoll (a hydrophilic polysaccharide) is heavier than PBMCs but less dense than granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils) and erythrocytes (red blood cells). So following centrifugation in the presence of ficoll, you obtain a top layer of plasma, followed by a lower layer of PBMCs and then a fraction of polymorphonuclear cells (such as neutrophils and eosinophils) and finally a bottom layer of erythrocytes. The polymorphonuclear cells can be further isolated by lysing the red blood cells.
The centrifugation steps (spins) remove the plasma from the whole blood, which stays on top of the layer. The peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) settle just below the plasma, while red blood cells and granulocytes settle after the PBMCs.
If using the specialised Sepmate tube, you can tip the entire top layer (plasma and PBMCs) into a new tube the wash the blood cells with phosphate buffered saline (PBS).
If you are not using a specialised tube, then carefully aspirate the PBMCs and wash with PBS in subsequent steps.
Washed PBMCs can be stored in RNA-preserving reagents such as RNAlater or freezing media. Freezing media is made up of 10% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) in Fetal calf serum for downstream applications.
When freezing cells, the goal is to do so in a controlled, gentle manner. You can achieve this by placing the cells in a temperature-controlling environment such as a Mr Frosty. Such cell freezing containers are filled with Isopropanol, which allows the temperature to drop by one degree celsius/min when placed at ultra-low temperatures (liquid nitrogen).
Buffy coat = platelets and white blood cells (leukocytes)
PBMCs are widely used in research and toxicology applications.
Application: PBMCs allow you to study immune responses to certain stimuli. To do this, you may stimulate a PBMC culture with agents that are known to modulate the immune system and then assess the outcome. Assessment can be done via proteomics (Mass-spectrometry), flow cytometry(study each population via fluorescence-assisted cell sorting) or Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA).
Because peripheral blood is the place where exposure to chemicals occurs, PBMCs are prone to be influenced by drugs and chemicals. This is why the availability of PBMCs from peripheral blood is very important for researchers studying toxicity of new drugs or chemical compounds.
Side-by-side comparison studies; researchers typically need both normal PBMCs and diseased PBMCs to compare in side-by-side studies, to get to the molecular heart of a specific toxic response. Understanding which pathways or molecules are impacted helps drug research proceed more rapidly, with greater efficaciousness and low immuntoxicity (Side-by-side comparison studies; researchers typically need both normal PBMCs and diseased PBMCs to compare in side-by-side studies, to get to the molecular heart of a specific toxic response. Understanding which pathways or molecules are impacted helps drug research proceed more rapidly, with greater efficaciousness and low immuntoxicity (Jalal Pourahmad and Ahmad Salimi; Iran J Pharm Res. 2015 Autumn; 14(4): 979).
//
//MUSIC
Music: Shine by Joakim Karud
http://joakimkarud.com/use-my-music/
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
This video is about isolating peripheral blood mononuclear cells, peripheral blood samples, peripheral blood lymphocytes, pbmc, pbmc isolation, pbmc cells, pbmc isolation protocol, pbmc processing







Информация по комментариям в разработке