A more convenient way to find if any molecule is optically active or inactive is to find the elements of symmetry in that molecule. if any of the elements of symmetry, such as a plane of symmetry, a center of symmetry or an axis of symmetry is present in the molecule, then the molecule is symmetrical, i.e., it will be superimposable on its mirror image and hence it will be optically inactive. If all the elements of symmetry are absent, then the molecule will be non-superimposable on its mirror image and it will exist in optically active forms.
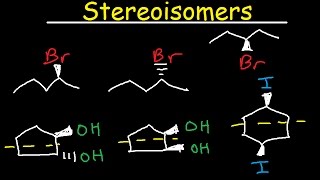
The plane of Symmetry: (Mirror Plan): A plane of symmetry is an imaginary plane that passes through a molecule such that atoms or groups of atoms on one side of the plane form a mirror image of those on the other side. It is particularly useful if the molecule contains two or more chiral centers. Consider the molecule of tartaric acid, It contains two chiral centers (indicated by red color). This structure and its mirror image represent a pair of enantiomers. And Both are optically active. But the third Structure has a (horizontal) plane of symmetry and so that the upper and lower parts of the molecule are mirror images of each other. Thus in spite of the fact that tartaric acid contains two chiral centers, structure (III) is optically inactive. Such a form is known as meso- or i-form. It is optically inactive due to internal compensation. i.e., rotation due to one asymmetric carbon is canceled by the other.
Centre of symmetry: (Inversion Centre): A center of symmetry is defined as a point in a molecule from which lines when drawn on opposite sides at equal distance, meet exactly similar points (groups or atoms) in the molecule. For example the isomer of 2 4-dimethyl cyclobutane -1,3-dicarboxylic acid possesses a center of symmetry, Thus, in spite of the fact that the molecule has four asymmetric carbon atoms, it is optically inactive because of the presence of the center of symmetry represented. Another example of a molecule having a center of symmetry is dimethyl diketo piperazine. This compound has two asymmetric carbon atoms and at the same time it also exists in two geometrical isomeric forms, i.e., cis and trans forms, The cis - isomer has no element of symmetry and therefore it exists in two enantiomeric forms. The trans-isomer has a center of symmetry and hence it is optically inactive.
Alternating Axis of Symmetry (Improper rotation axis): A molecule is said to possess a n-fold alternating axis of symmetry if, on rotating through an angle of 360° about this axis and followed by a reflection of the resulting molecule in a plane perpendicular to the axis, then the mirror image is exactly identical to the original molecule. If A = C then the molecule contains a n fold axis of symmetry. And If A ≠ C then the molecule does not contain n fold axis of symmetry. Consider the molecule of 1, 2, 3, 4 -tetramethyl cyclobutane (I). It contains four asymmetric carbon atoms. This molecule contains four-fold alternating axis of symmetry. Rotation of structure (I) through 90° about the axis, which passes through the center of the ring and perpendicular to its plane, gives (II). A reflection of this in a plane perpendicular to the axis gives (III), which is exactly identical to (I). Therefore the molecule is said to possess a four-fold alternating axis of symmetry. Another example is 3, 4, 3’, 4’ - tetramethyl spiro-(1, 1)-di pyrrolidinium p-toluene sulphonate (IV). It does not contain any plane of symmetry, but it contains four-fold alternating axis of symmetry. If(IV) is rotated through 90° about the central axis, of both rings, FOLLOWING structure is obtained. A reflection of this through the central plane perpendicular to this axis gives a molecule identical in every respect with the first one.
Gaseous State - Physical Chemistry
• Postulates of Kinetic Molecular Theor...
Colloidal States - Physical Chemistry
• What is Colloidal Solution? | Colloid...
Stereochemistry - Organic Chemistry
• Explain Configuration and Conformatio...
Nanomaterials - Engineering Chemistry
• Compare top down with bottom up Proce...
Water and Its Treatment - Engineering Chemistry
• Explain why hard water gives out a cu...
Electrochemistry - Engineering Chemistry
• Distinguish between metallic and elec...
Environmental Studies
• MCQ on Environmental Studies Part 8
Optics - Applied Physics
• What are cartesian sign conventions f...
For Details Visit
http://cepekmedia.co.nf
http://cepek.hol.es/
http://edmerls.66Ghz.com/
http://edmerls.tk/









Информация по комментариям в разработке