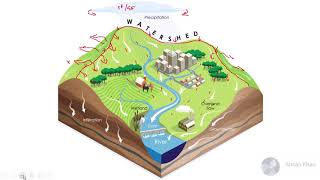
A catchment area is a term used in geography and environmental studies to describe the area of land that drains water into a particular body of water, such as a river, lake, or ocean. It is also known as a drainage basin, watershed, or river basin.
In this video, we will explore what a catchment area is and how it works.
What is a Catchment Area?
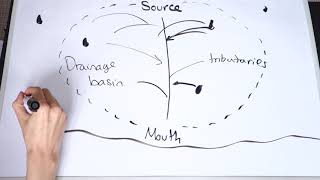
A catchment area is a geographic region that is defined by the natural boundaries of a river or other water body. It is the area of land from which all surface and groundwater flows into a particular watercourse or water body. This includes all the streams, creeks, and tributaries that flow into the main river, as well as the surrounding land that contributes to the flow of water.
Catchment areas can range in size from small watersheds that drain a few square kilometers of land, to large river basins that encompass thousands of square kilometers. They are usually defined by the topography of the land, with the highest points of the watershed forming the boundaries of the catchment area.
How Does a Catchment Area Work?
The function of a catchment area is to collect, store, and transport water from precipitation, such as rainfall and snowmelt, to a particular body of water. This process is driven by the natural hydrological cycle, which involves the continuous movement of water between the atmosphere, land, and oceans.
When rain falls or snow melts, the water is absorbed by the ground, flows into rivers and streams, or percolates down into underground aquifers. In a catchment area, the flow of water is controlled by the topography of the land, with water flowing downhill from higher elevations to lower elevations.
As water flows through the catchment area, it interacts with the natural environment, picking up nutrients, sediments, and pollutants along the way. This can have significant impacts on the quality and quantity of water in the catchment area, as well as the health of the ecosystems that depend on it.
Why are Catchment Areas Important?
Catchment areas are important for a variety of reasons, including:
Water Management: Catchment areas are essential for managing water resources, as they provide the source of water for many human uses, such as drinking water, irrigation, and industrial processes. By understanding the flow of water in a catchment area, water managers can develop strategies to ensure a sustainable and reliable supply of water.
Ecosystem Protection: Catchment areas are critical for the protection and conservation of natural ecosystems, as they provide habitat for a wide range of plant and animal species. By managing the flow of water and reducing pollutants, we can help to maintain the health and diversity of these ecosystems.
Flood and Drought Mitigation: Catchment areas can help to mitigate the impact of extreme weather events, such as floods and droughts. By managing the flow of water in a catchment area, we can reduce the risk of flooding downstream, while also ensuring that there is enough water available during periods of drought.
Climate Change Adaptation: Catchment areas can play an important role in mitigating the impacts of climate change, such as sea level rise and changes in precipitation patterns. By protecting and restoring catchment areas, we can help to reduce the risk of flooding and erosion, while also improving water quality and biodiversity.
In conclusion, catchment areas are an essential component of our natural environment, providing the source of water for many human uses and supporting a wide range of natural ecosystems.
Like the content of this channel?
Subscribe to the channel and help others watch: / shaooraaa
Instagram: www.instagram.com/shaoorkhan








Информация по комментариям в разработке