Check out Bas Rutten's Liver Shot on MMA Surge: http://bit.ly/MMASurgeEp1
Mahalo biology expert Mary Poffenroth explains the classification system of species and the taxonomic hierarchy.
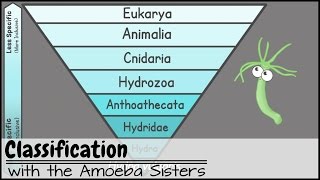
The Taxonomic Hierarchy
---------------------------------------------------------------------
In biological taxonomy, all life forms can be classified within a hierarchal system that orders them from the broadest, most inclusive categories to the narrowest, most exclusive. The most widely used conventional categories are domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species.http://www.biology-online.org/diction...
This taxonomic system was initially pioneered by
Carl Linnaeus in the 18th century. Linnaeus used Latin terms to arrange species according to observable similarities and differences in their physical morphology. With recent innovations in molecular biology, the traditional classification system has been made more precise by the possibility of going beyond superficial similarities and mapping similarities and differences between species at the genetic level.
Following this hierarchy, the highest level, domain, distinguishes between bacteria and organisms with a true cell nucleus. The next level down, kingdom, distinguishes plants from animals. Below the kingdom level, at the level of phylum, we can differentiate between vertebrates and creatures with no backbone. Among the vertebrates, you can differentiate mammals from birds, fish and reptiles at the class level. Among mammals, you can differentiate between ones that eat meat and ones that don't. Some mammals belong to the order
Carnivora, meaning they eat meat. Others belong to the order Herbivora, meaning they feed exclusively on vegetation. Next, humans belong to the family Hominidae, which includes great apes (gorillas, orangutans and chimpanzees). At the genus level, we are related to now-extinct species of early humans, such as the Neanderthals. Finally, at the lowest level of the biological taxonomy, all living humans are members of the same species, since we form a single reproductive population sharing the capacity to produce children, regardless of superficial racial differences. • Learn Biology: Classification- The Ta...
Classification of a Sample Species
---------------------------------------------------------------------
In order to form a clearer idea of these categories, it is helpful to think of a specific example, like a mountain lion.
At the domain level, a mountain lion belongs to the category of
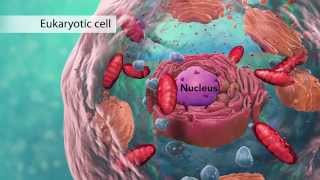
Eukarya, which are organisms with a cellular nucleus, unlike bacteria. At the kingdom level, it is Animalia, as opposed to a plant or a fungus. Mountain lions belong to the phylum Chordata, which are animals that have a backbone, in contrast to Arthropoda (spiders) or Porifera (sponges).
The c
lass Mammalia includes animals that have fur and produce milk. This is the level at which fish, birds and reptiles are distinguished. Mountain lions belong to the order Carnivora along with other meat eaters such as bears and wolves. Their family, Felidae, includes large cats including leopard or lions. At the next level down, the genus Puma includes jaguars and cougars but not tigers.Finally, mountain lions constitute a distinct species, concolor. When designating a particular species, it is customary to use the genus and species name. So the short taxonomic designation for a mountain lion is Puma concolor. • Learn Biology: Classification- The Ta...
Read more by visiting our page at:
http://www.mahalo.com/learn-biology-c...








Информация по комментариям в разработке